Understanding And Managing Rib Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever experienced a sharp twinge or persistent ache in your rib area? Many people have, and it's a sensation that can range from mildly annoying to severely debilitating. Rib pain can be a mysterious condition, presenting itself without an apparent cause, leaving sufferers puzzled and seeking answers. The complexity of the rib cage, which houses vital organs and supports the upper body, means that rib pain can arise from a multitude of factors, each requiring a unique approach for diagnosis and treatment. In this guide, we'll delve deep into the intricacies of rib pain, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the best ways to manage and prevent it.
Rib pain can be caused by a variety of ailments, from injuries and fractures to infections and even underlying medical conditions. It's not uncommon for individuals to overlook the early signs of rib pain, assuming it to be a minor inconvenience. However, understanding the root cause is crucial, as it could be indicative of an underlying health issue that requires immediate attention. This article aims to shed light on the different aspects of rib pain, providing you with the knowledge needed to identify and address it effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the anatomy of the rib cage, common causes and symptoms of rib pain, as well as diagnostic methods and treatment options. We'll also address frequently asked questions about rib pain, offering insights into prevention strategies and when to seek professional medical advice. Whether you're dealing with rib pain yourself or seeking information for a loved one, this article is designed to equip you with the expertise needed to navigate this often perplexing condition.
Read also:Rare King Von Autopsy Picture Revealed A Tragic Aftermath
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Rib Cage
- Common Causes of Rib Pain
- Symptoms of Rib Pain
- Diagnosing Rib Pain
- Treatment Options for Rib Pain
- Preventive Measures
- When to See a Doctor
- Rib Pain in Children
- Psychological Aspects of Rib Pain
- Alternative Therapies
- Physical Therapy and Exercises
- Diet and Nutrition
- Impact of Rib Pain on Daily Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Rib Cage
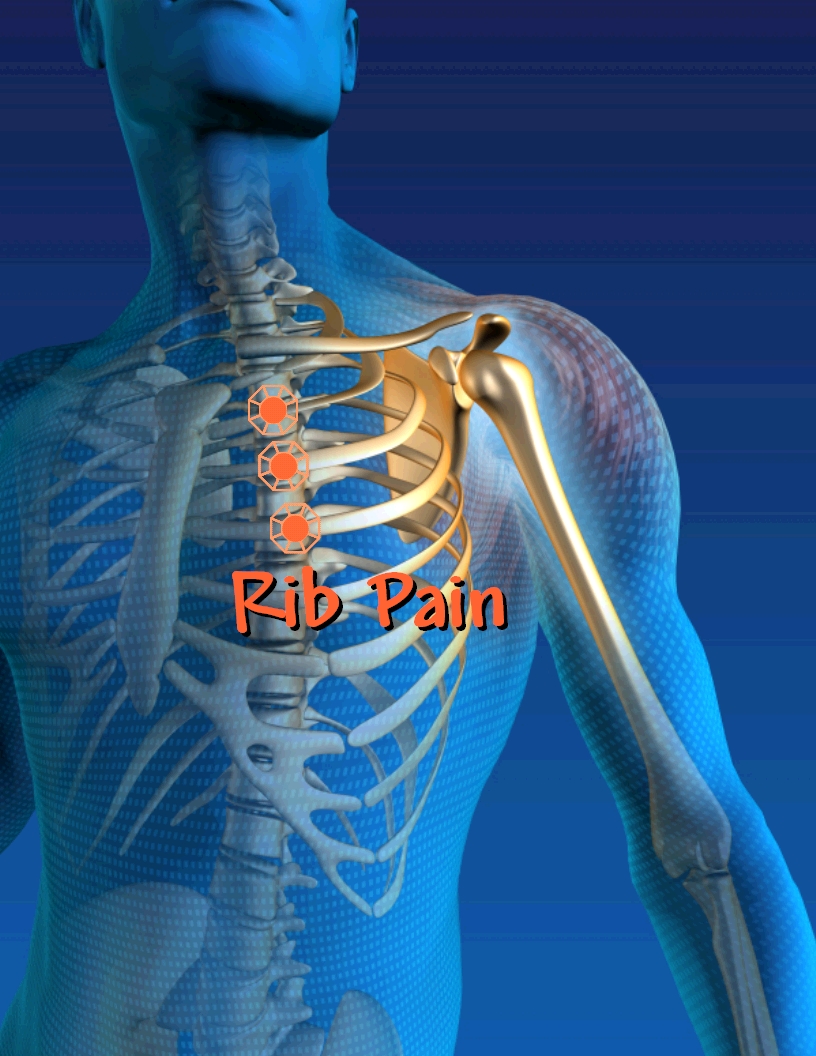
The rib cage is a complex structure composed of bones and cartilage that forms a protective enclosure for vital organs such as the heart and lungs. It consists of 12 pairs of ribs, the sternum (breastbone), and the thoracic vertebrae in the spine. The upper seven ribs are known as "true ribs" because they attach directly to the sternum, while the lower five are referred to as "false ribs" and "floating ribs" depending on their attachment points. This intricate design allows the rib cage to provide both support and flexibility, essential for breathing and upper body movements.
The ribs are connected to the spine at the back and to the sternum via costal cartilage at the front, enabling the chest to expand and contract during respiration. The intercostal muscles, located between the ribs, play a crucial role in this process, assisting in the mechanics of breathing. Understanding the anatomy of the rib cage is fundamental in diagnosing rib pain, as it helps identify the source of discomfort, whether it's related to bone, cartilage, muscle, or nerve issues.
In addition to protecting the thoracic organs, the rib cage serves as an attachment point for many muscles involved in movement and posture. The diaphragm, a major muscle for respiration, is anchored to the lower ribs, while muscles such as the pectoralis major and minor, latissimus dorsi, and abdominal muscles also have connections to the rib cage. This anatomical complexity underscores the importance of a thorough examination when assessing rib pain, as it could be linked to various musculoskeletal or visceral conditions.
Common Causes of Rib Pain
Rib pain can stem from numerous causes, each with its own set of characteristics and treatment approaches. The most frequent causes include trauma, such as fractures or bruises from accidents or falls. These injuries can lead to significant discomfort and require appropriate medical intervention to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Another prevalent cause of rib pain is costochondritis, an inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum. This condition is often characterized by sharp, localized pain that can mimic heart-related issues, leading to anxiety and further complications if not properly diagnosed. Costochondritis is typically self-limiting but may require pain management strategies to alleviate symptoms.
Pleurisy, an inflammation of the pleura (the lining surrounding the lungs), is another potential cause of rib pain. This condition can result from infections, autoimmune disorders, or other underlying health issues, causing sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing. Identifying the root cause of pleurisy is essential for effective treatment and recovery.
Read also:Where Is Abby Lee Miller Now Uncovering Her Current Whereabouts
Additionally, rib pain may be related to muscle strains, particularly in athletes or individuals engaging in repetitive physical activities. Poor posture, especially during prolonged periods of sitting or working at a desk, can also contribute to rib pain by straining the muscles and ligaments supporting the rib cage. Recognizing these lifestyle factors is crucial in developing preventive measures and addressing the pain effectively.
Finally, rib pain can sometimes be a symptom of more severe health conditions, such as osteoporosis, arthritis, or even cancer. These cases require a comprehensive medical evaluation to determine the appropriate course of action and ensure the best possible outcomes for the patient.
Symptoms of Rib Pain
The symptoms of rib pain can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Common indicators include sharp or dull pain in the rib area, tenderness to touch, and difficulty breathing or moving. Some individuals may experience referred pain, where discomfort is felt in areas such as the back or shoulders, complicating the diagnosis process.
In cases of rib fractures or bruises, pain is often exacerbated by movement, coughing, or deep breathing. Swelling and bruising around the affected area may also be present, providing visual clues to the nature of the injury. It's important to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen, as untreated fractures can lead to complications such as lung injuries or infections.
Costochondritis typically presents as localized pain and tenderness in the chest area, often mistaken for cardiac-related issues. This condition tends to improve with rest and pain management, but persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.
Pleurisy can manifest as sharp, stabbing pain in the chest that intensifies with breathing or coughing. Accompanying symptoms may include shortness of breath, a dry cough, or fever, depending on the underlying cause. Prompt medical assessment is crucial to address the root cause and prevent further complications.
Muscle strains and sprains around the rib cage can lead to discomfort that worsens with movement or exertion. This type of pain is often associated with physical activities or poor posture, and alleviating it typically involves rest, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Understanding the specific symptoms of rib pain is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Diagnosing Rib Pain
The diagnostic process for rib pain begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. A healthcare provider will inquire about the onset, duration, and nature of the pain, as well as any recent injuries or activities that may have contributed to the condition. This information helps narrow down potential causes and guides further diagnostic testing.
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, are often employed to visualize the structure of the rib cage and identify any fractures, dislocations, or other abnormalities. These tests provide valuable insights into the extent and nature of the injury, informing the appropriate treatment approach.
In cases where rib pain is suspected to be related to internal conditions, additional tests such as blood work, ultrasound, or pulmonary function tests may be conducted. These assessments help identify potential underlying health issues, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, or respiratory problems, that could be contributing to the pain.
For conditions like costochondritis or pleurisy, a thorough examination of the chest and respiratory system is essential to rule out cardiac or pulmonary causes. This may involve techniques such as auscultation (listening to the chest with a stethoscope) and percussion (tapping on the chest to assess the underlying structures).
The diagnostic process for rib pain is multifaceted, requiring a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and specialized tests to determine the root cause. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan and ensuring the best possible outcome for the patient.
Treatment Options for Rib Pain
Treatment for rib pain depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In cases of fractures or bruises, initial management typically involves rest, ice application, and pain relief medications to alleviate discomfort and promote healing. Severe fractures may require immobilization or surgical intervention to ensure proper alignment and recovery.
For costochondritis, pain management is the primary focus, with over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and heat application often providing relief. Physical therapy and stretching exercises may also be recommended to improve flexibility and reduce strain on the rib cage.
Pleurisy treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, such as infections or inflammation. This may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, or other targeted therapies. In some cases, procedures such as thoracentesis (removal of excess fluid from the pleural space) may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and improve breathing.
Muscle strains and sprains around the rib cage typically respond well to rest, ice or heat application, and gentle stretching exercises. Strengthening the muscles supporting the rib cage can also help prevent future injuries and reduce the risk of recurrence.
In all cases, a tailored treatment plan developed in collaboration with a healthcare provider is essential for addressing rib pain effectively. This may involve a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies to ensure optimal recovery and long-term health.
Preventive Measures
Preventing rib pain involves adopting lifestyle modifications and habits that reduce the risk of injuries and strain on the rib cage. Maintaining good posture, especially during prolonged periods of sitting or working at a desk, is crucial for minimizing stress on the rib muscles and ligaments.
Engaging in regular physical activity, including exercises that strengthen the core and upper body muscles, can help support the rib cage and reduce the likelihood of injuries. Conditioning exercises that improve flexibility and balance are also beneficial for preventing falls and accidents that could lead to rib fractures or bruises.
Using appropriate protective equipment during sports or high-impact activities is essential for safeguarding the rib cage from injuries. This includes wearing helmets, pads, or guards as necessary, depending on the specific sport or activity.
For individuals with underlying health conditions that predispose them to rib pain, such as osteoporosis or arthritis, managing these conditions effectively is vital for reducing the risk of fractures and other complications. This may involve medications, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring by a healthcare provider.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of rib pain and maintain optimal rib health and function.
When to See a Doctor
While some cases of rib pain may resolve with self-care and home remedies, certain situations warrant prompt medical attention. If rib pain is accompanied by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or severe pain that does not improve with rest and pain relief measures, seeking medical evaluation is crucial to rule out serious conditions.
Individuals who experience rib pain following an injury or trauma, such as a fall or accident, should also seek medical assessment to determine the extent of the injury and prevent complications. Persistent or worsening rib pain, especially if it interferes with daily activities or sleep, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
In cases where rib pain is associated with other concerning symptoms, such as fever, unexplained weight loss, or persistent cough, further investigation is necessary to identify any underlying health issues that may require targeted interventions.
Timely medical evaluation of rib pain can help identify the root cause, guide appropriate treatment, and prevent potential complications, ensuring the best possible outcomes for the patient.
Rib Pain in Children
Children may experience rib pain due to various causes, ranging from injuries during play or sports to respiratory or inflammatory conditions. Understanding the unique aspects of rib pain in children is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Injuries, such as rib fractures or bruises, are common causes of rib pain in children, often resulting from falls or accidents. Prompt medical evaluation and appropriate treatment are crucial to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Respiratory conditions, such as asthma or pneumonia, can also contribute to rib pain in children, often presenting with symptoms like coughing or difficulty breathing. Identifying and managing these conditions effectively is essential for alleviating rib pain and improving overall health.
Costochondritis, an inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum, may occur in children, causing localized chest pain. This condition is typically self-limiting and responds well to rest and pain relief measures.
Addressing rib pain in children requires a comprehensive approach that considers the child's age, activity level, and overall health. Collaboration with a pediatric healthcare provider is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and ensuring optimal outcomes for the child.
Psychological Aspects of Rib Pain
Rib pain can have a significant impact on an individual's mental and emotional well-being, particularly when it interferes with daily activities or persists over time. Understanding the psychological aspects of rib pain is crucial for providing comprehensive care and support to those affected.
Chronic rib pain can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or depression, especially if the pain is severe or poorly managed. This emotional distress may exacerbate the perception of pain, creating a cycle of discomfort and psychological distress.
Addressing the psychological aspects of rib pain involves a holistic approach that includes pain management, emotional support, and coping strategies. Techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and cognitive behavioral therapy can help individuals manage their emotional responses to pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Collaboration with mental health professionals may also be beneficial for individuals experiencing significant psychological distress related to rib pain. Providing comprehensive support that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of rib pain can enhance recovery and promote long-term well-being.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional medical treatments, alternative therapies may offer complementary benefits for individuals experiencing rib pain. These therapies can provide additional pain relief, promote relaxation, and support overall health and well-being.
Acupuncture, an ancient practice involving the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body, may help alleviate rib pain by promoting the release of endorphins and improving circulation. This therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic or persistent pain.
Chiropractic care, which focuses on the alignment of the spine and musculoskeletal system, may also offer relief for rib pain, especially when related to postural issues or muscle imbalances. Gentle adjustments and manipulations can help improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
Massage therapy can provide relaxation and pain relief by targeting tense or strained muscles around the rib cage. This therapy may be particularly beneficial for individuals with muscle-related rib pain or those experiencing stress-related tension.
Engaging in alternative therapies should be done in consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and compatibility with other treatments. Incorporating these therapies into a comprehensive care plan can enhance recovery and improve overall well-being.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery and management of rib pain, particularly for individuals with injuries or chronic conditions affecting the rib cage. A tailored physical therapy program can help improve strength, flexibility, and overall function, reducing the risk of future injuries and promoting long-term health.
A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise regimen that targets the specific needs and goals of the individual. This may include strengthening exercises for the core and upper body muscles, stretching routines to improve flexibility, and conditioning exercises to enhance endurance and balance.
Breathing exercises can also be an integral part of physical therapy for rib pain, helping individuals improve respiratory function and reduce tension in the rib cage. These exercises can be particularly beneficial for individuals with respiratory conditions or those experiencing stress-related rib pain.
Regular participation in physical therapy and exercise programs can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with rib pain, promoting recovery and enhancing overall quality of life. Collaboration with a qualified physical therapist is essential for developing a safe and effective program tailored to the individual's needs.
Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in supporting overall health and well-being, including the management of rib pain. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can promote healing, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body's ability to recover from injuries or conditions affecting the rib cage.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly beneficial for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health and reducing the risk of fractures, particularly for individuals with conditions like osteoporosis. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are excellent sources of these nutrients.
Staying hydrated is also crucial for overall health and can support the body's natural healing processes. Drinking sufficient water and consuming hydrating foods, such as fruits and vegetables, can help maintain optimal hydration levels.
Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide valuable guidance and support for individuals seeking to improve their diet and nutrition as part of their rib pain management plan. A personalized approach to diet and nutrition can enhance recovery and promote long-term health.
Impact of Rib Pain on Daily Life
Rib pain can have a profound impact on an individual's daily life, affecting physical, emotional, and social well-being. Understanding the challenges and finding ways to manage them is crucial for maintaining a high quality of life despite the presence of pain.
Physically, rib pain can limit mobility and make routine activities, such as lifting, bending, or even breathing, difficult and uncomfortable. This can lead to decreased physical activity and overall fitness, further contributing to the cycle of pain and discomfort.
Emotionally, persistent rib pain can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, or depression, particularly if the pain interferes with work, hobbies, or social interactions. Addressing these emotional challenges is essential for promoting mental health and well-being.
Socially, rib pain can impact relationships and participation in social activities, leading to feelings of isolation or withdrawal. Finding ways to stay connected with friends, family, and support networks is important for maintaining a sense of belonging and emotional support.
By adopting a comprehensive approach to managing rib pain, individuals can find ways to overcome these challenges and maintain a fulfilling and active lifestyle. Collaboration with healthcare providers, support networks, and mental health professionals can provide the necessary support and resources for managing the impact of rib pain on daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common causes of rib pain?
Common causes of rib pain include injuries (such as fractures or bruises), costochondritis, pleurisy, muscle strains, and underlying health conditions like osteoporosis or arthritis.
2. How is rib pain diagnosed?
Rib pain is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies (such as X-rays or CT scans). Additional tests may be conducted to identify underlying health issues.
3. What are some home remedies for managing rib pain?
Home remedies for rib pain include rest, ice or heat application, over-the-counter pain relievers, and gentle stretching exercises. It's important to consult a healthcare provider for persistent or severe pain.
4. Can rib pain be a sign of a serious condition?
In some cases, rib pain can be a sign of a serious condition, such as a heart attack, pulmonary embolism, or cancer. Prompt medical evaluation is essential to rule out these conditions and ensure appropriate treatment.
5. Are alternative therapies effective for rib pain?
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy, may offer complementary benefits for rib pain management. It's important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure safety and compatibility with other treatments.
6. How can I prevent rib pain?
Preventive measures for rib pain include maintaining good posture, engaging in regular physical activity, using protective equipment during sports, and managing underlying health conditions effectively.
Conclusion
Rib pain is a complex condition with a wide range of causes and symptoms, requiring a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. By understanding the underlying factors and adopting a tailored treatment plan, individuals can effectively address rib pain and improve their overall health and well-being. Through preventive measures, lifestyle modifications, and collaboration with healthcare providers, it's possible to minimize the impact of rib pain and maintain a fulfilling, active life. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can navigate the challenges of rib pain with confidence and resilience.
For further information and resources on rib pain, consider visiting reputable medical websites or consulting with healthcare professionals specializing in musculoskeletal and thoracic health.
Remember, early intervention and comprehensive care are key to managing rib pain effectively and ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Article Recommendations