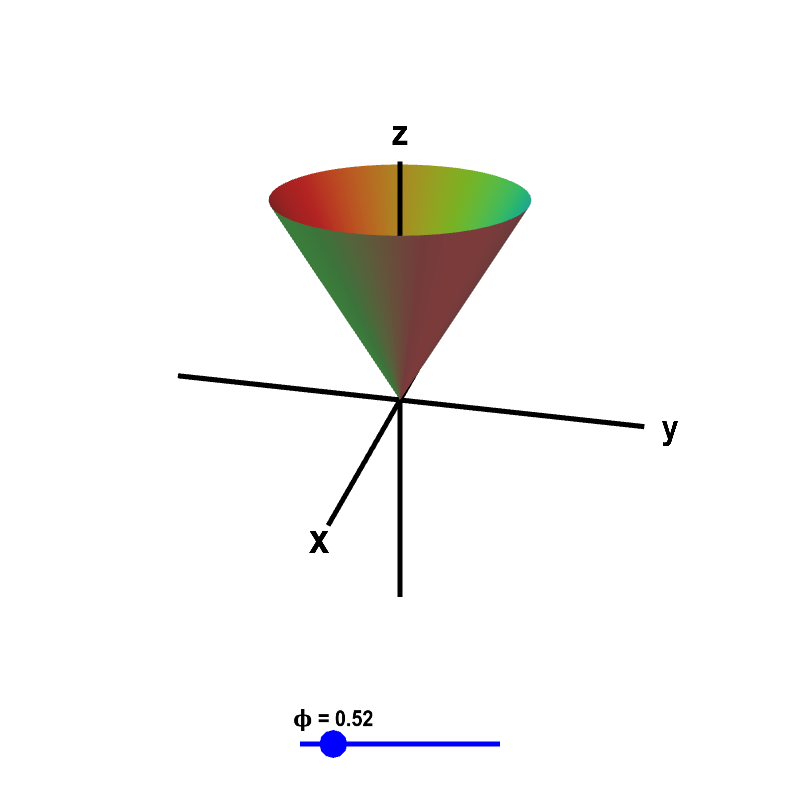
Exploring The Geometry Of A Cone In Spherical Coordinates
Cone in spherical coordinates is a fascinating topic that bridges the gap between geometry and calculus, allowing us to understand and visualize three-dimensional shapes in a more intuitive way. As we dive into the world of spherical coordinates, we uncover how this system redefines our comprehension of a cone, presenting it in a format that can simplify complex mathematical problems. By converting standard Cartesian coordinates into spherical coordinates, we can better analyze the properties and characteristics of conical shapes in various applications such as physics, engineering, and computer graphics.
In a typical Cartesian coordinate system, the representation of a cone can appear cumbersome and less relatable. However, spherical coordinates offer a perspective that can make this geometric shape more comprehensible. By using a combination of angles and radial distances, we can represent points on the surface of a cone with greater efficiency. This approach not only facilitates calculations but also enhances our ability to visualize and manipulate these shapes in space.
As we delve deeper into the concept of a cone in spherical coordinates, we will explore its mathematical definitions, applications, and implications in various fields. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or simply someone intrigued by the beauty of mathematics, understanding how cones are represented in spherical coordinates will enrich your knowledge and appreciation for the subject.
Read also:Unlocking The Inspirational Power Of Wednesday Quotes
What is the Definition of a Cone in Spherical Coordinates?
A cone in spherical coordinates can be defined based on its geometric properties and the relationships between its dimensions. In spherical coordinates, a point in three-dimensional space is represented by three variables: the radial distance (r), the polar angle (θ), and the azimuthal angle (φ). For a cone, these relationships can be expressed as:
- Radial distance (r): This represents the distance from the origin to the point on the cone's surface.
- Polar angle (θ): This angle, measured from the positive z-axis, describes the cone's inclination.
- Azimuthal angle (φ): This angle describes the rotation around the z-axis.
By using these parameters, one can derive the equation of a cone in spherical coordinates. For a cone with a vertex at the origin and opening upwards, the relationship can be expressed as:
r = k * cos(θ)
where k is a constant that determines the cone's opening angle. This equation illustrates the fundamental relationship between the radial distance and the angle of inclination.
How Do You Convert Cartesian Coordinates to Spherical Coordinates for a Cone?
Converting Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) to spherical coordinates (r, θ, φ) involves the following equations:
- r = √(x² + y² + z²)
- θ = cos⁻¹(z/r)
- φ = tan⁻¹(y/x)
To visualize a cone in spherical coordinates, it is essential to understand how these transformations affect the representation of the cone's surface. By applying these conversions, we can see how the dimensions of the cone relate to the angles and distances in spherical coordinates.
Read also:Who Is Zendaya Dating An Indepth Look At Her Relationship Status
What are the Applications of Cones in Spherical Coordinates?
The applications of cones in spherical coordinates extend across various fields, including:
- Physics: In optics, conical shapes are used to describe light propagation and reflection.
- Engineering: Cones are prevalent in mechanical design, often serving as structural components in machinery.
- Computer Graphics: The representation of cones in 3D modeling is crucial for rendering realistic objects and environments.
Understanding cones in spherical coordinates enhances our ability to solve problems in these disciplines, leading to more efficient design and analysis.
How Do You Visualize a Cone in Spherical Coordinates?
Visualizing a cone in spherical coordinates requires a grasp of the three-dimensional space and how the angles and distances interact. By plotting points according to the spherical coordinate system, one can create a model of a cone that illustrates its surface and dimensions. Software tools and graphing calculators can assist in rendering these visualizations, providing a clearer understanding of the geometry involved.
What Challenges Are Associated with Working with Cones in Spherical Coordinates?
While the concept of a cone in spherical coordinates is useful, several challenges may arise, including:
- Complexity: The equations can become complex, making it difficult to derive certain properties.
- Visualization: Seeing the cone in three-dimensional space requires skill and experience.
- Calculations: Integrating and differentiating functions involving cones can be challenging.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of understanding cones in spherical coordinates often outweigh the difficulties.
What Are Some Examples of Cones in Spherical Coordinates?
To illustrate the concept further, consider the following examples of cones represented in spherical coordinates:
- A right circular cone with a vertex at the origin and an opening angle of 45 degrees can be described by the equation r = z.
- A cone with a vertex at the origin and a slant height that varies can be expressed as r = k * sin(θ), where k is a constant.
- A cone describing a physical object, such as a funnel, can be modeled using specific parameters tailored to the object's geometry.
Each of these examples highlights the versatility of the spherical coordinate system in representing conical shapes.
How Can You Further Your Understanding of Cones in Spherical Coordinates?
To deepen your understanding of cones in spherical coordinates, consider the following resources:
- Textbooks on advanced geometry and calculus.
- Online courses focusing on multivariable calculus and spherical coordinates.
- Software tools like MATLAB or GeoGebra for visualizing mathematical concepts.
- Research papers exploring applications of spherical coordinates in various fields.
By engaging with these resources, you can enhance your knowledge and skills in working with cones in spherical coordinates.
In conclusion, the study of a cone in spherical coordinates not only expands our mathematical toolkit but also enriches our understanding of geometry in three-dimensional space. By mastering the concepts discussed, individuals can apply these principles in various scientific and engineering contexts, paving the way for innovative solutions and insights.
Article Recommendations