Understanding Postpartum Preeclampsia: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered about the potential complications that can arise after childbirth? One condition that might not be on your radar is postpartum preeclampsia, a serious health concern that can affect new mothers. Although it's less common than other postpartum issues, it demands attention due to its potentially severe consequences. This article aims to shed light on postpartum preeclampsia, its symptoms, causes, treatments, and preventive measures, providing a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
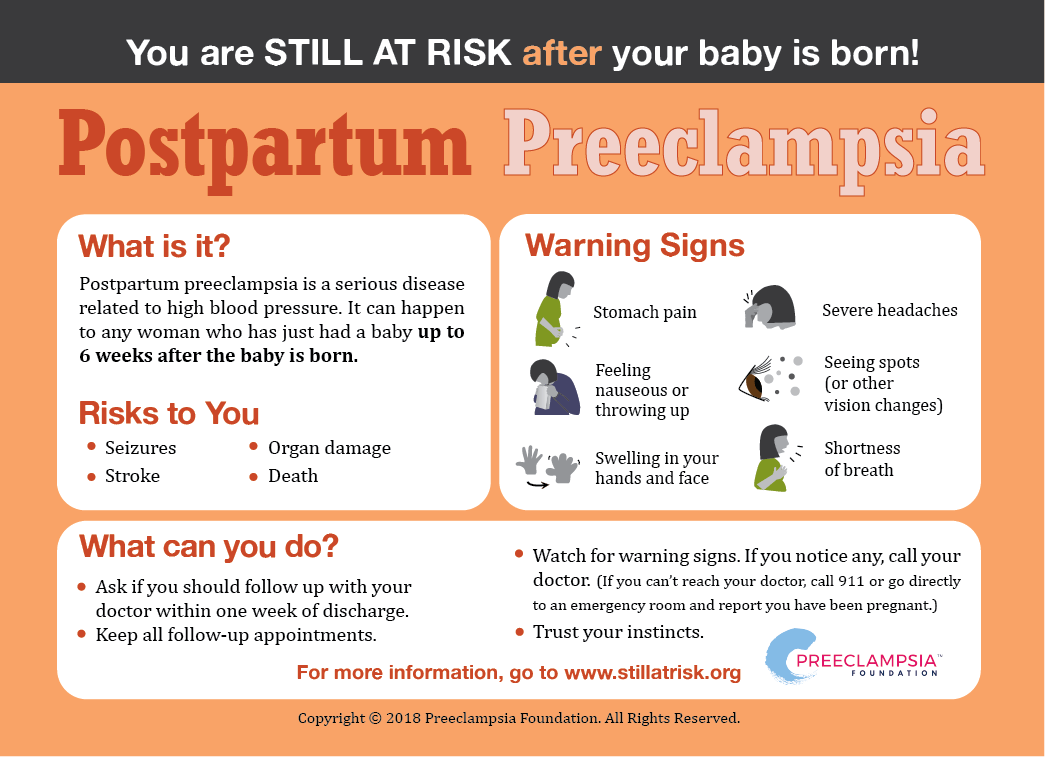
Postpartum preeclampsia can occur in women who have recently given birth, even if they didn't show signs of preeclampsia during pregnancy. The condition is characterized by high blood pressure and excess protein in the urine, which can lead to serious complications such as stroke, seizures, and organ damage. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve outcomes for affected women.
In this article, we'll explore the ins and outs of postpartum preeclampsia, starting with what it is, its symptoms, causes, and risk factors. We'll then delve into the diagnostic process, treatment options, and ways to prevent this condition. Additionally, we'll address frequently asked questions and provide reliable resources for further reading. Whether you're a new mother, a healthcare professional, or someone interested in maternal health, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to understand and manage postpartum preeclampsia effectively.
Read also:Dallas House Of Blues A Unique Live Music Experience
Table of Contents
- What is Postpartum Preeclampsia?
- Symptoms of Postpartum Preeclampsia
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Diagnosing Postpartum Preeclampsia
- Treatment Options
- Preventive Measures
- Impact on Maternal Health
- Importance of Follow-Up Care
- Emotional and Psychological Effects
- Support Systems and Resources
- Postpartum Preeclampsia Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Postpartum Preeclampsia?
Postpartum preeclampsia is a condition that arises after childbirth, characterized by high blood pressure and an excess of protein in the urine. Unlike preeclampsia, which occurs during pregnancy, postpartum preeclampsia develops after the delivery of the baby, typically within 48 hours but can occur up to six weeks postpartum. It is a rare but serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
In postpartum preeclampsia, the body experiences an abnormal response to the physiological changes that occur after childbirth. This response can lead to complications such as seizures (eclampsia), stroke, organ damage, and even death if not promptly treated. The condition is part of a spectrum of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, which are leading causes of maternal morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of postpartum preeclampsia is still an ongoing area of research. However, it is generally believed that the factors contributing to preeclampsia during pregnancy, such as abnormal placentation, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction, may also play a role in its postpartum manifestation. Additionally, hormonal and vascular changes that occur after delivery may exacerbate these conditions, leading to the development of postpartum preeclampsia.
Key Characteristics
- Onset after childbirth, typically within 48 hours but possibly up to six weeks postpartum.
- Characterized by high blood pressure (140/90 mmHg or higher) and proteinuria (excess protein in the urine).
- May lead to serious complications like seizures, stroke, and organ damage if untreated.
Historical Context
The understanding of postpartum preeclampsia has evolved over time. Historically, it was considered a continuation of preeclampsia that occurs during pregnancy. However, medical advancements have led to recognizing it as a distinct condition with its own challenges and treatment protocols. This recognition has been pivotal in improving maternal outcomes and reducing the incidence of severe complications associated with the condition.
Symptoms of Postpartum Preeclampsia
Recognizing the symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia is crucial for timely intervention. The symptoms can vary in intensity and may resemble other postpartum conditions, making diagnosis challenging. However, certain hallmark signs can help differentiate it from other postpartum issues.
Common Symptoms
- High Blood Pressure: One of the primary indicators, high blood pressure, is typically 140/90 mmHg or higher.
- Proteinuria: The presence of excess protein in the urine, often identified through a urine test.
- Severe Headaches: Persistent or severe headaches that do not respond well to pain relievers.
- Vision Changes: Blurred vision, light sensitivity, or temporary loss of vision.
- Swelling: Sudden swelling of the face, hands, or feet.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Unexplained nausea or vomiting, particularly when accompanied by other symptoms.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, which may be related to fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema).
- Abdominal Pain: Pain, particularly in the upper right side of the abdomen.
Less Common Symptoms
- Chest Pain: A feeling of tightness or pain in the chest.
- Sudden Weight Gain: Rapid weight gain due to fluid retention.
- Reduced Urine Output: Decreased frequency or volume of urination.
It's important to note that the presence of one or more of these symptoms doesn't necessarily mean a woman has postpartum preeclampsia. However, if these symptoms are severe or persist, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly to rule out or confirm the diagnosis.
Read also:Roberts Field Airport Redmond Your Gateway To Central Oregon
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of postpartum preeclampsia remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its development. Understanding these can help identify women at higher risk and guide preventive measures.
Potential Causes
- Placental Factors: Abnormalities in the placenta during pregnancy can continue to affect the mother's body after delivery.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of preeclampsia or related conditions can increase the risk.
- Hormonal Changes: The rapid hormonal shifts post-delivery may play a role in triggering the condition.
- Immune System Response: Inflammatory processes and immune system responses can contribute to the development of the condition.
Risk Factors
- History of Preeclampsia: Women who had preeclampsia during pregnancy are at higher risk.
- First Pregnancy: First-time mothers are more likely to develop postpartum preeclampsia.
- Obesity: Higher body mass index (BMI) is associated with increased risk.
- Multiple Gestations: Carrying twins or more increases the risk.
- Age: Women over 35 or under 20 are at greater risk.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or kidney disease heighten the risk.
- Race and Ethnicity: African American women are at a higher risk compared to other ethnic groups.
Identifying these risk factors is essential for healthcare providers to monitor at-risk women closely and implement preventive strategies during and after pregnancy.
Diagnosing Postpartum Preeclampsia
Diagnosing postpartum preeclampsia involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and monitoring of symptoms. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Clinical Evaluation
- Medical History: A thorough review of the patient's medical history, including any history of preeclampsia during pregnancy, is essential.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam to check for signs of high blood pressure, swelling, and other symptoms is typically the first step.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels to detect hypertension.
- Urine Test: Testing for proteinuria to confirm the presence of excess protein in the urine.
- Blood Tests: Assessing liver function, kidney function, and platelet levels to identify any abnormalities.
Additional Diagnostic Tools
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like an ultrasound or CT scan may be used to assess the severity of the condition.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To evaluate heart function, especially if there are symptoms of chest pain or shortness of breath.
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to managing postpartum preeclampsia effectively and preventing severe complications such as eclampsia, stroke, or organ failure.
Treatment Options
Treating postpartum preeclampsia involves managing symptoms, preventing complications, and addressing any underlying conditions. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual's needs and the severity of the condition.
Medications
- Antihypertensives: Medications such as labetalol, nifedipine, or hydralazine are commonly used to control high blood pressure.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Administered to prevent seizures (eclampsia) in women with severe preeclampsia.
- Diuretics: May be used to reduce fluid retention and swelling in some cases.
Monitoring and Supportive Care
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring of blood pressure, urine output, and other vital signs is essential.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for close monitoring and treatment.
- Rest and Stress Reduction: Encouraging rest and minimizing stress to aid recovery.
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
- Dietary Changes: A low-sodium diet and increased intake of fruits and vegetables can help manage blood pressure.
- Physical Activity: Gradual reintroduction of physical activity as advised by healthcare providers.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight to reduce risk factors.
It's important for women with postpartum preeclampsia to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and promotes recovery.
Preventive Measures
While postpartum preeclampsia can't always be prevented, certain measures can help reduce the risk and promote overall maternal health.
Pre-Pregnancy Planning
- Health Assessment: A thorough health assessment before pregnancy to identify and manage underlying conditions.
- Weight Management: Achieving a healthy weight and maintaining it throughout pregnancy.
During Pregnancy
- Regular Prenatal Care: Consistent prenatal visits to monitor health and address any concerns promptly.
- Monitoring Blood Pressure: Regular blood pressure checks to detect any early signs of preeclampsia.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in safe physical activity.
Postpartum Care
- Postpartum Check-Ups: Attending scheduled postpartum appointments to monitor recovery and address any symptoms.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Being vigilant about recognizing symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia and seeking medical attention if needed.
By taking these preventive measures, women can reduce their risk of developing postpartum preeclampsia and promote better overall maternal health.
Impact on Maternal Health
Postpartum preeclampsia can have significant implications for maternal health, affecting both physical and emotional well-being. Understanding these impacts is crucial for providing comprehensive care and support to affected women.
Physical Health Effects
- Cardiovascular Health: Persistent high blood pressure can lead to long-term cardiovascular issues if not managed properly.
- Organ Function: Damage to organs such as the liver, kidneys, or brain can occur in severe cases.
- Reproductive Health: Women with a history of postpartum preeclampsia may face increased risks in future pregnancies.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The experience of postpartum preeclampsia can be overwhelming and stressful, leading to emotional and psychological challenges.
- Anxiety and Depression: The stress of dealing with a serious health condition can contribute to anxiety or depression.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: Some women may experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) following a severe episode.
- Impact on Bonding: Physical and emotional challenges may affect bonding with the newborn.
Addressing these impacts requires a holistic approach that includes medical treatment, emotional support, and mental health resources. Providing comprehensive care can help women recover physically and emotionally, improving their quality of life and well-being.
Importance of Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is an essential component of managing postpartum preeclampsia, ensuring that women receive the necessary support and monitoring to promote recovery and prevent complications.
Postpartum Appointments
- Regular Check-Ups: Scheduled postpartum appointments to monitor blood pressure and overall health.
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Continued monitoring to ensure blood pressure levels return to normal.
- Laboratory Tests: Follow-up tests to assess organ function and rule out any lingering issues.
Long-Term Monitoring
- Cardiovascular Health: Ongoing monitoring of cardiovascular health to prevent future complications.
- Future Pregnancy Planning: Guidance and monitoring for women planning future pregnancies to minimize risks.
By prioritizing follow-up care, healthcare providers can help women manage postpartum preeclampsia effectively, reducing the risk of long-term health issues and promoting overall well-being.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Postpartum preeclampsia can have profound emotional and psychological effects on women, impacting their mental health and overall well-being. Addressing these effects is crucial for comprehensive care and recovery.
Common Psychological Challenges
- Anxiety and Depression: The stress of managing a serious health condition can contribute to feelings of anxiety or depression.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: Women may experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) following a severe episode of postpartum preeclampsia.
- Impact on Self-Identity: The experience of postpartum preeclampsia can affect a woman's sense of self and identity as a mother.
Strategies for Emotional Support
- Counseling and Therapy: Access to mental health services, such as counseling or therapy, to address emotional and psychological challenges.
- Support Groups: Participation in support groups for women who have experienced postpartum preeclampsia to share experiences and gain support.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating mindfulness practices, meditation, or relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
By addressing the emotional and psychological effects of postpartum preeclampsia, healthcare providers can support women's recovery and help them navigate the challenges of motherhood with resilience and confidence.
Support Systems and Resources
Having access to robust support systems and resources is essential for women recovering from postpartum preeclampsia. These resources can provide valuable information, emotional support, and practical assistance to enhance recovery and well-being.
Healthcare Support
- Primary Care Providers: Ongoing communication with healthcare providers to monitor health and address any concerns.
- Specialist Care: Access to specialists, such as cardiologists or nephrologists, for managing specific health issues.
Community and Peer Support
- Support Groups: Joining support groups for women who have experienced postpartum preeclampsia to share experiences and gain insights.
- Community Resources: Utilizing local resources, such as parenting classes or postpartum support programs, to gain knowledge and skills.
Online Resources
- Educational Websites: Accessing reputable websites for information on postpartum preeclampsia and maternal health.
- Online Forums: Participating in online forums or communities to connect with others and share experiences.
By leveraging these support systems and resources, women can empower themselves with knowledge, connect with others who have similar experiences, and access the necessary support to navigate their recovery journey successfully.
Postpartum Preeclampsia Research
Research on postpartum preeclampsia is crucial for advancing understanding, improving diagnosis and treatment, and ultimately enhancing outcomes for affected women. Ongoing research efforts are focused on several key areas.
Understanding the Pathophysiology
- Mechanisms of Disease: Investigating the underlying mechanisms that contribute to the development of postpartum preeclampsia.
- Genetic and Molecular Factors: Exploring genetic and molecular factors that may predispose women to the condition.
Improving Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnostic Tools: Developing new diagnostic tools and techniques to improve early detection and diagnosis.
- Innovative Treatments: Exploring novel treatment approaches to enhance management and reduce complications.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
- Preventive Strategies: Identifying and evaluating preventive strategies to reduce the risk of postpartum preeclampsia.
- Public Health Initiatives: Implementing public health initiatives to raise awareness and promote maternal health.
By investing in research and innovation, the medical community can continue to make strides in understanding and managing postpartum preeclampsia, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for women worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is postpartum preeclampsia?
Postpartum preeclampsia is a condition that occurs after childbirth, characterized by high blood pressure and excess protein in the urine. It can lead to serious complications if not promptly treated.
- When does postpartum preeclampsia typically occur?
Postpartum preeclampsia usually develops within 48 hours after delivery but can occur up to six weeks postpartum.
- What are the symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia?
Common symptoms include high blood pressure, proteinuria, severe headaches, vision changes, swelling, nausea, and shortness of breath.
- How is postpartum preeclampsia treated?
Treatment involves managing symptoms with medications such as antihypertensives and magnesium sulfate, as well as supportive care and lifestyle modifications.
- Can postpartum preeclampsia be prevented?
While it can't always be prevented, risk factors can be managed through pre-pregnancy planning, regular prenatal care, and monitoring during and after pregnancy.
- What is the long-term impact of postpartum preeclampsia?
Postpartum preeclampsia can have long-term effects on cardiovascular health and may increase the risk of complications in future pregnancies.
Conclusion
Postpartum preeclampsia is a serious condition that requires awareness, timely diagnosis, and effective management to prevent complications and promote maternal health. By understanding its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options, women and healthcare providers can work together to ensure the best possible outcomes. Ongoing research and support systems play a crucial role in advancing knowledge and improving care for women affected by this condition. With the right information and resources, women can navigate their recovery journey with confidence and resilience, ensuring a healthy and fulfilling postpartum experience.
For further information, please refer to reputable sources such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the Preeclampsia Foundation.
Article Recommendations