Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential: An In-Depth Exploration
The saturated calomel electrode (SCE) is a vital component in electrochemistry, serving as a reference electrode for various measurements. It is often employed in potentiometric titrations and as a reference point in electrochemical cells. Understanding the saturated calomel electrode potential is crucial for anyone involved in electrochemical research or applications. This article delves into the significance, functioning, and applications of the saturated calomel electrode potential, illuminating its role in contemporary science.
The saturated calomel electrode potential is derived from the equilibrium established between mercury and mercurous chloride (calomel) in a saturated KCl solution. This equilibrium is highly stable and provides a consistent reference point for measuring electrode potentials. As we explore this topic, we will address common queries regarding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of the saturated calomel electrode potential, emphasizing its importance in laboratory settings.
With the increasing reliance on electrochemical measurements in various fields such as environmental science, materials science, and biomedical applications, it becomes essential to understand the underlying principles of the saturated calomel electrode potential. This knowledge equips researchers and practitioners with the ability to make informed decisions when selecting reference electrodes and interpreting electrochemical data.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To The Pageant St Louis
What is the Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential?
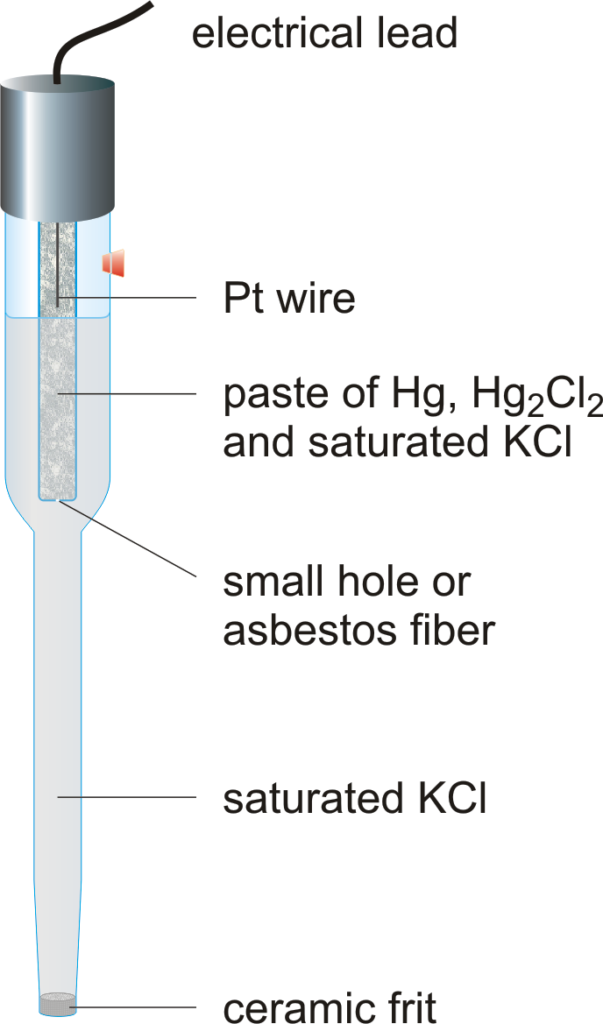
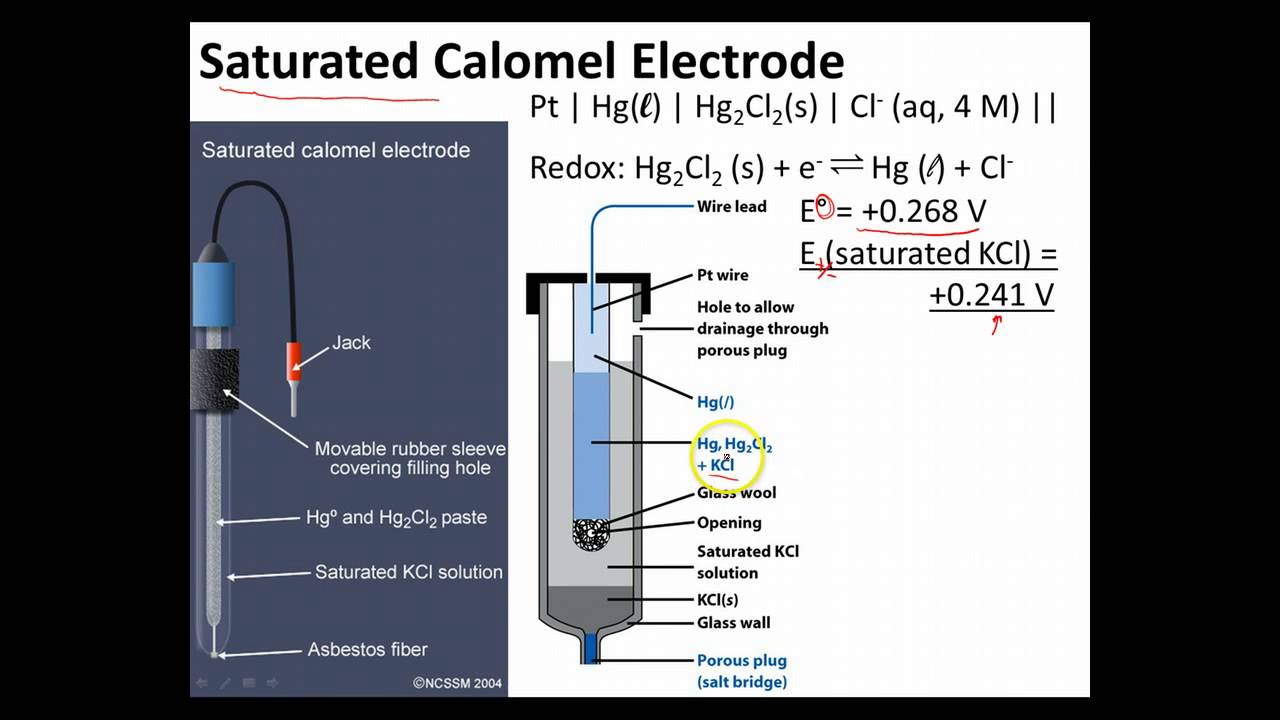
The saturated calomel electrode potential refers to the potential difference between the saturated calomel electrode and a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) under specified conditions. The SCE is typically composed of mercury in contact with mercurous chloride and a saturated solution of potassium chloride. The potential of the SCE is approximately +0.244 V at 25°C, making it a reliable reference point for various electrochemical measurements.
How Does the Saturated Calomel Electrode Work?
The functioning of the saturated calomel electrode relies on a chemical reaction that takes place between the mercury and mercurous chloride in the presence of a saturated KCl solution. The overall reaction can be represented as:
Hg2Cl2 (s) + 2e- ⇌ 2Hg (l) + 2Cl- (aq)
This reaction establishes a constant equilibrium, which enables the SCE to maintain a stable potential. The electrode potential can be influenced by temperature and concentration, but it remains relatively constant due to the saturation of KCl.
What are the Advantages of Using the Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential?
- Stable and reproducible potential under standard conditions
- Widely recognized and accepted reference electrode in electrochemistry
- Relatively simple construction and maintenance
- Compatible with a range of electrochemical measurements
What are the Limitations of the Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential?
Despite its advantages, the saturated calomel electrode potential has some limitations:
- Contains toxic mercury, posing environmental and health risks
- Potential can vary with temperature and concentration
- Not suitable for all types of electrochemical experiments
How Do You Prepare a Saturated Calomel Electrode?
Preparing a saturated calomel electrode involves several steps:
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Non Perishable Food A Pantry Essential
- Gather materials: mercury, mercurous chloride (calomel), potassium chloride, and a suitable container.
- Fill the container with a saturated potassium chloride solution.
- Add a layer of mercurous chloride to the bottom of the container.
- Carefully introduce mercury into the container, ensuring it covers the mercurous chloride.
- Seal the container to prevent contamination and evaporation.
What Applications Use the Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential?
The saturated calomel electrode potential finds applications across various fields, including:
- Analytical chemistry for potentiometric titrations
- Corrosion studies to assess the corrosion potential of materials
- Electroplating and electrochemical deposition processes
- Environmental monitoring to measure ion concentrations
How Does the Saturated Calomel Electrode Compare to Other Reference Electrodes?
When comparing the saturated calomel electrode potential to other reference electrodes, such as the silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrode, several factors come into play:
- Stability: SCE offers a more stable potential under varying conditions.
- Toxicity: SCE contains toxic mercury, while Ag/AgCl is safer to handle.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Both electrodes can be affected by temperature, but SCE is generally more robust.
Conclusion: Why is the Saturated Calomel Electrode Potential Important?
In conclusion, the saturated calomel electrode potential plays a crucial role in electrochemistry as a reliable reference point for various measurements. Understanding its functioning, advantages, and limitations is essential for researchers and practitioners in the field. As we continue to explore and innovate within the realm of electrochemical science, the importance of the saturated calomel electrode potential remains steadfast, guiding our understanding and applications in diverse areas.
Article Recommendations