Understanding GPU Memory Bus: The Backbone Of Graphics Performance
The GPU memory bus plays a crucial role in determining the performance and efficiency of graphics processing units (GPUs). As technology continues to advance, the demand for higher graphical fidelity and faster rendering speeds is ever-increasing. The GPU memory bus is a critical component that connects the GPU to its memory, impacting how data is transferred and processed. Understanding the intricacies of the GPU memory bus can help users make informed decisions when building or upgrading their computing systems.
In the realm of gaming, content creation, and data visualization, the speed and bandwidth of the GPU memory bus can significantly influence performance outcomes. A wider bus can lead to enhanced data throughput, which is essential for handling high-resolution textures and complex rendering tasks. Thus, both casual users and professionals alike should have a keen insight into how the GPU memory bus functions and what specifications to look for when selecting a graphics card.
Moreover, as we delve deeper into the architecture of modern GPUs, it becomes evident that the design of the memory bus is not merely a technical specification but a fundamental aspect that dictates the overall efficiency of the graphics pipeline. With various advancements such as GDDR6 and HBM2 memory technologies, the GPU memory bus has evolved to meet the increasing demands of contemporary applications, making it a pivotal topic for anyone interested in maximizing their system’s graphical capabilities.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Understanding What Does Imk Mean And How To Use It
What is a GPU Memory Bus?
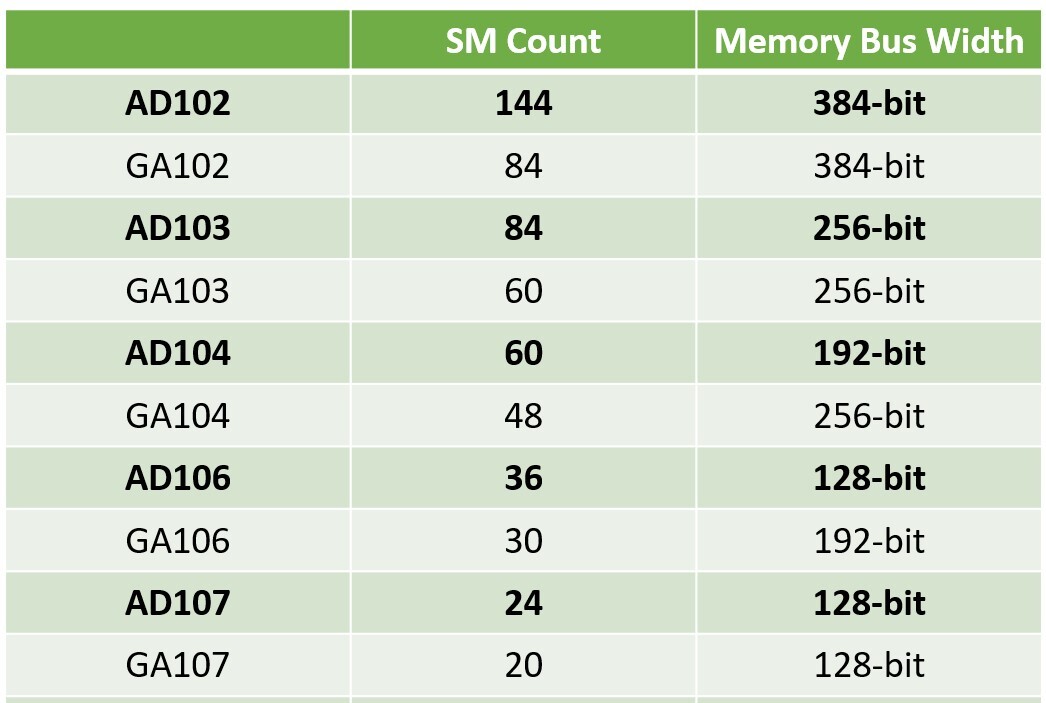
The GPU memory bus is a channel that connects the GPU to its video memory (VRAM). It is responsible for transferring data between the two, which is crucial for rendering images and processing graphics. The width of the memory bus, typically measured in bits, determines how much data can be transferred at once. Common memory bus widths include 128-bit, 256-bit, and 384-bit, with wider buses allowing for more data to be processed simultaneously.
How Does the GPU Memory Bus Impact Performance?
Performance in gaming and graphics-intensive applications can be heavily influenced by the GPU memory bus. A wider bus means higher bandwidth, which is essential for handling large textures, complex models, and high frame rates. Here are the key factors:
- Data Transfer Rates: A wider memory bus allows for more data to be transferred per clock cycle.
- Texture Loading: Faster memory bandwidth results in quicker loading of textures and assets, reducing lag.
- Multi-tasking: High bandwidth enables smoother performance when running multiple applications or processes simultaneously.
What Are the Different Types of GPU Memory Buses?
There are several types of memory buses used in GPUs, each designed for specific performance requirements:
- GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate): Commonly used in most consumer graphics cards, providing good performance for gaming.
- HBM (High Bandwidth Memory): Utilized in high-end GPUs for professional applications, offering superior bandwidth and efficiency.
- DDR (Double Data Rate): While primarily used for system memory, some older GPUs may utilize DDR memory buses.
Why Is Memory Bus Width Important?
The width of the memory bus directly correlates with the amount of data transferred at any given moment. A wider memory bus can provide the following advantages:
- Increased Bandwidth: More data can be processed simultaneously, leading to improved performance.
- Better Multitasking: With higher bandwidth, the GPU can handle more tasks at once without a significant drop in performance.
- Improved Frame Rates: A wider memory bus can lead to higher frame rates in demanding gaming scenarios.
How Does Clock Speed Affect GPU Memory Bus Performance?
The clock speed of the memory bus, measured in MHz, determines how fast data can be transferred. The combination of bus width and clock speed ultimately defines the total bandwidth available:
- Higher Clock Speeds: Can improve the speed of data transfers, enhancing performance.
- Optimal Balance: The best performance is achieved when both width and speed are maximized.
Can Upgrading the GPU Memory Bus Improve My System?
Upgrading to a GPU with a wider memory bus can yield noticeable performance improvements, especially in graphics-intensive applications. However, it’s essential to consider the following:
Read also:The Intricacies Of A First Date Navigating Expectations And Etiquette
- Compatibility: Ensure that the new GPU is compatible with your motherboard and power supply.
- Overall System Balance: Upgrading the GPU alone may not provide a significant boost if other components are outdated.
Conclusion: Maximizing GPU Performance with the Right Memory Bus
In the realm of graphics processing, the GPU memory bus serves as a crucial element that can make or break performance. Whether you are a gamer, a content creator, or a professional in need of high-end graphics capabilities, understanding the specifications and functionality of the GPU memory bus is essential. By considering factors such as memory bus width, clock speed, and overall compatibility, users can make informed decisions that lead to enhanced performance and a more satisfying experience in their respective fields.
Article Recommendations