Understanding Spin Doublet Example In Quantum Mechanics
The concept of spin doublets plays a crucial role in the field of quantum mechanics, particularly in understanding the behavior of particles at a subatomic level. Spin doublets refer to pairs of particles that possess half-integer spin values, which leads to intriguing implications in particle physics and quantum field theory. This article delves into the intricacies of spin doublets, exploring foundational concepts, real-world applications, and notable examples that illuminate this fascinating aspect of quantum mechanics.
In quantum mechanics, particles are described not only by their mass and charge but also by their intrinsic angular momentum, known as spin. The notion of spin doublets arises when we consider particles that exist in states of superposition, allowing them to behave in ways that defy classical intuition. Understanding these doublets is essential for grasping more complex phenomena, such as particle interactions and the formation of composite particles like baryons and mesons.
As we journey through this article, we will examine various examples of spin doublets, their mathematical representations, and their significance in modern physics. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of what spin doublets are and why they matter in the broader context of quantum theory.
Read also:Unveiling The Curly Bob A Timeless Chic Hair Trend
What Are Spin Doublets?
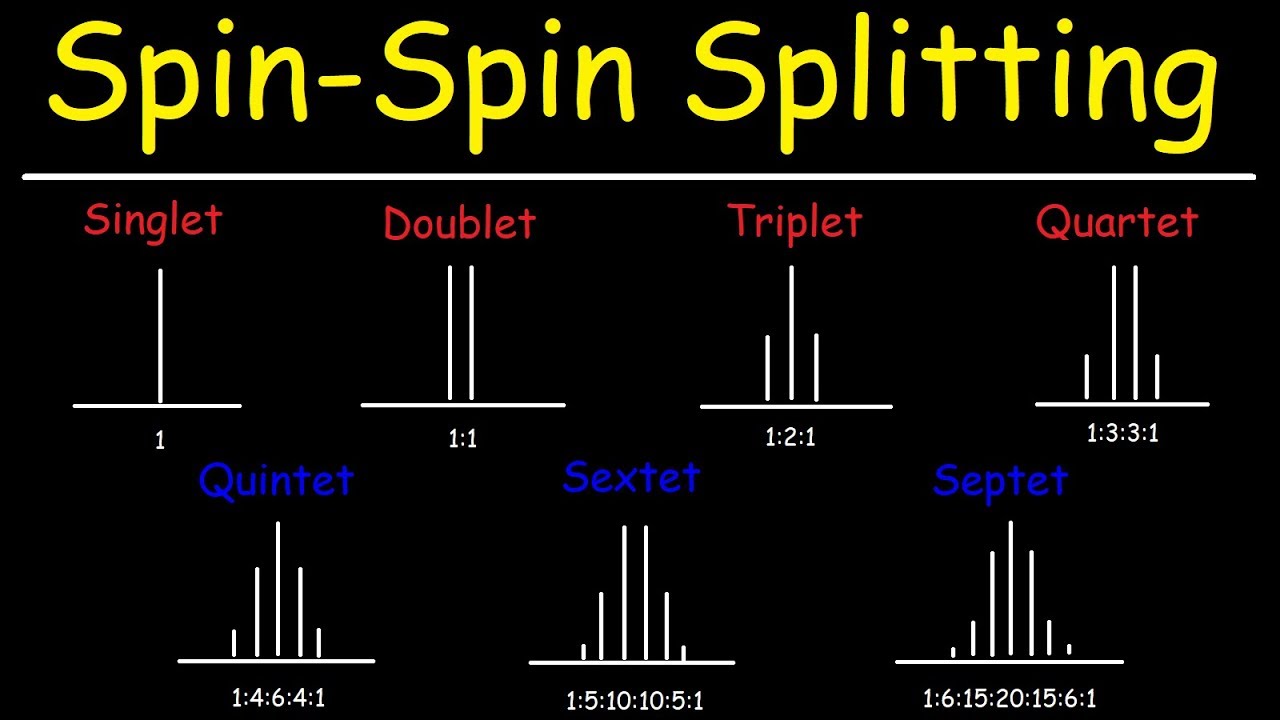
Spin doublets are pairs of particles that share certain quantum characteristics, particularly their spin values. Specifically, a spin doublet consists of two particles that each possess spin-1/2, which means they can exist in two possible states: spin-up and spin-down. These states can be represented mathematically using quantum mechanics' formalism. The significance of spin doublets lies in their ability to interact with external fields, such as magnetic fields, in unique ways.
How Do Spin Doublets Work in Quantum Mechanics?
In quantum mechanics, the behavior of particles is often described using wave functions, which encapsulate all possible states of a system. For spin doublets, the wave function can be expressed as a linear combination of the individual spin states of the particles involved. This combination leads to various observable phenomena, such as quantum entanglement and superposition.
What Are Some Real-World Examples of Spin Doublets?
- Electron-Positron Pair: In particle physics, an electron and its antiparticle, the positron, form a spin doublet. Both particles have a spin of 1/2 and exhibit unique behaviors when interacting with external forces.
- Neutrino Families: The three known types of neutrinos (electron, muon, and tau neutrinos) also form spin doublets with their corresponding charged leptons. This relationship has important implications for understanding weak interactions in particle physics.
What Is the Mathematical Representation of Spin Doublets?
Mathematically, spin doublets can be represented using Dirac spinors. A Dirac spinor is a complex vector that encapsulates the spin states of a particle. In the case of a spin doublet, the Dirac spinor contains two components, each representing one of the spin states. This representation is essential for understanding how spin doublets interact with other particles and fields.
How Do Spin Doublets Relate to Particle Physics?
In particle physics, spin doublets play a crucial role in the classification of fundamental particles. For instance, the Standard Model of particle physics organizes particles into multiplets based on their spin and other quantum numbers. Spin doublets are a vital component of this organization, influencing how particles interact through the weak nuclear force.
Can You Give a Spin Doublet Example in Nature?
A notable spin doublet example in nature can be found in the behavior of quarks, the fundamental constituents of protons and neutrons. Quarks come in six flavors and possess fractional electric charges and spin-1/2. When quarks combine to form baryons, such as protons and neutrons, they exhibit properties that can be understood through the lens of spin doublets. The interactions between quarks and the strong force lead to the formation of these composite particles, which are essential for the structure of matter.
What Are the Implications of Spin Doublets in Quantum Field Theory?
In quantum field theory, the concept of spin doublets extends beyond individual particles to encompass fields that describe their interactions. For example, the electroweak theory, which unifies electromagnetic and weak forces, incorporates spin doublets in its framework. This unification has significant implications for understanding fundamental interactions and the behavior of particles at high-energy scales.
Read also:Discover The Real Name Of The Radiant Star Jojo Siwa
How Do Spin Doublets Influence Quantum Computing?
Spin doublets also find applications in the emerging field of quantum computing. Quantum bits, or qubits, can leverage the properties of spin doublets to perform calculations more efficiently than classical computers. By harnessing the superposition and entanglement properties of spin doublets, researchers are exploring new paradigms for information processing and storage.
What Future Research Is Being Conducted on Spin Doublets?
The study of spin doublets continues to be a vibrant area of research within the fields of particle physics, quantum mechanics, and condensed matter physics. Researchers are investigating the properties of spin doublets in various contexts, such as exploring their role in high-temperature superconductors or examining their implications for dark matter candidates. As our understanding of these phenomena deepens, new discoveries are likely to emerge, potentially reshaping our comprehension of the universe.
Conclusion: The Significance of Spin Doublets
In summary, the spin doublet example serves as a foundational concept in quantum mechanics and particle physics. By understanding the nature of spin doublets, we gain insights into the behavior of fundamental particles and their interactions. The implications of spin doublets extend to various fields, including quantum computing and high-energy physics, making them an essential area of study for future scientific exploration.
Article Recommendations