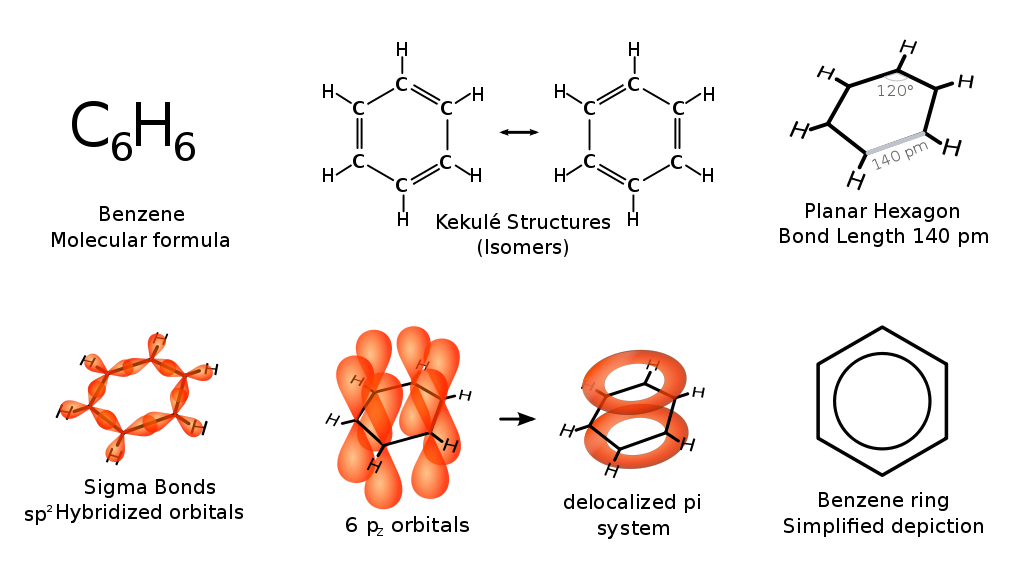Cyclohexane Vs Benzene: A Comprehensive Comparison
Cyclohexane and benzene are two important hydrocarbons that play significant roles in the field of chemistry and various industrial applications. While they share some structural similarities as cyclic compounds, their molecular structures, properties, and uses diverge in many important ways. Understanding these differences is crucial for chemists, engineers, and anyone interested in organic chemistry.
In this article, we will explore various aspects of cyclohexane and benzene, including their chemical structures, physical properties, and common applications. We will also delve into their safety profiles and environmental impacts, providing a well-rounded perspective on these two compounds. Ultimately, by the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of how cyclohexane and benzene compare and contrast with one another.
Whether you are a student seeking to grasp the basics of organic chemistry or a professional looking to refresh your knowledge, this article will serve as a valuable resource. Join us as we dissect the intriguing world of cyclohexane vs benzene, highlighting key differences and similarities that define these essential compounds.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Imdb Top 250 An Insightful Journey Into Cinemas Elite Rankings
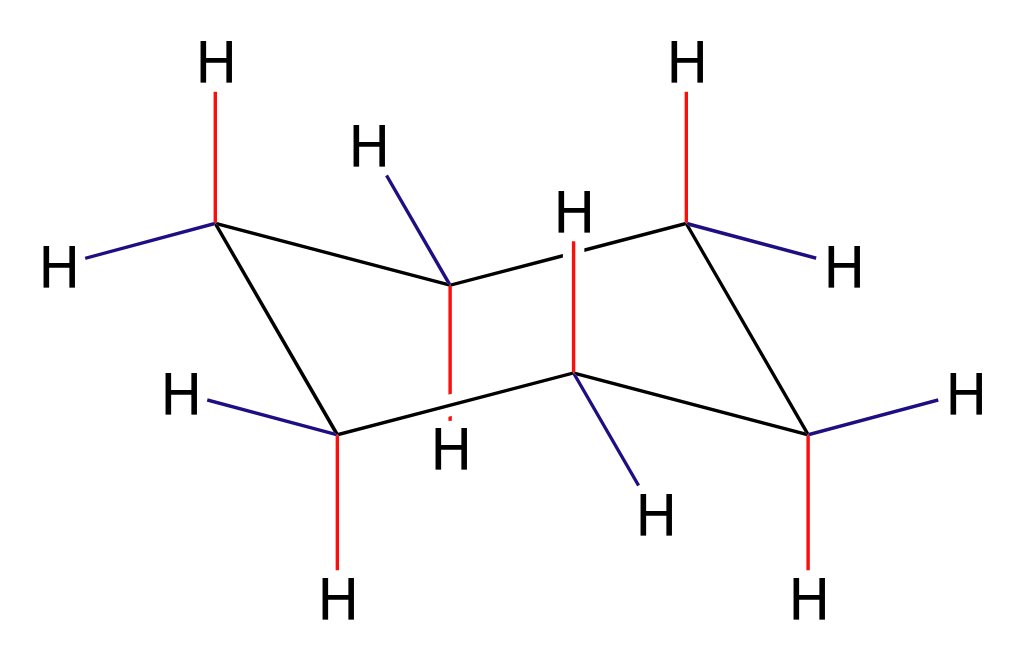
What is the Molecular Structure of Cyclohexane?
Cyclohexane is a saturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H12. Its structure consists of six carbon atoms arranged in a ring, with each carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This arrangement leads to a stable, non-aromatic compound that is free of double bonds. Cyclohexane can exist in multiple conformations, with the most stable form being the chair conformation, which minimizes steric strain and torsional strain between hydrogen atoms.
What is the Molecular Structure of Benzene?
Benzene, on the other hand, is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H6. The structure of benzene features six carbon atoms arranged in a planar ring, with alternating double bonds between the carbon atoms. This unique arrangement gives benzene its aromatic properties, characterized by a delocalization of electrons across the ring, which contributes to its chemical stability and reactivity.
How Do Cyclohexane and Benzene Differ in Physical Properties?
The physical properties of cyclohexane and benzene reveal significant differences that are important for their applications. Below are some key physical properties compared:
- Boiling Point: Cyclohexane has a boiling point of approximately 81 °C, while benzene boils at around 80 °C.
- Density: Cyclohexane is less dense than water, with a density of 0.81 g/cm³, whereas benzene has a density of 0.87 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Cyclohexane is non-polar and insoluble in water, while benzene is also non-polar but has a slightly higher solubility in organic solvents.
- Appearance: Cyclohexane is a colorless liquid with a distinctive detergent-like smell, while benzene is also a colorless liquid but has a sweet odor.
What Are the Common Uses of Cyclohexane?
Cyclohexane is widely used in various industrial applications, including:
- As a solvent for coatings, adhesives, and paints.
- In the production of nylon and other synthetic fibers.
- As a precursor in the synthesis of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone.
What Are the Common Uses of Benzene?
Benzene is a crucial starting material in the chemical industry, utilized for:
- Manufacturing various chemicals, including styrene, phenol, and aniline.
- Producing detergents, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
- As a solvent in laboratories and industrial processes.
How Do Cyclohexane and Benzene Compare in Terms of Safety?
Safety is a paramount concern when handling chemicals like cyclohexane and benzene. Cyclohexane is generally considered less hazardous compared to benzene, which is classified as a human carcinogen. Here are some safety considerations:
Read also:Discover The National Gallery Of Art East Building A Masterpiece Of Architecture And Art
- Cyclohexane: While it can cause irritation to the skin and eyes, it has a lower risk of long-term health effects.
- Benzene: Exposure can lead to serious health risks, including bone marrow damage and an increased risk of leukemia.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Cyclohexane and Benzene?
Both cyclohexane and benzene have environmental implications, but they differ in severity. Cyclohexane is less toxic to aquatic life compared to benzene, which can persist in the environment and contribute to air and water pollution. Regulations surrounding the use and disposal of benzene are stricter due to its carcinogenic nature.
Which Compound is More Versatile: Cyclohexane or Benzene?
When considering versatility, benzene often takes the lead due to its role as a foundational compound in organic synthesis. Its derivatives, such as toluene and xylene, are widely used in various chemical processes. Cyclohexane, while important, is primarily utilized for specific applications, particularly in the production of nylon and other synthetic materials.
In conclusion, understanding the differences and similarities between cyclohexane and benzene is essential for professionals in the field of chemistry and related industries. While both compounds share a cyclic structure, their distinct properties, applications, and safety profiles underscore the importance of choosing the right compound for specific needs. The debate of cyclohexane vs benzene continues to be relevant as industries evolve and seek safer, more efficient materials for their processes.
Article Recommendations