Mastering Git: How To Successfully Add An Empty Folder
When working with Git, many developers encounter the challenge of managing empty folders. Unlike files, Git does not track empty directories by default, which can lead to confusion when trying to maintain a clean project structure. Understanding how to effectively use the command "git add empty folder" is essential for keeping your repository organized. This article will guide you through the process of adding empty folders in Git, explore the reasons behind Git's behavior, and provide some handy tips to streamline your workflow.
In the world of software development, version control systems like Git play a crucial role in project management. However, one of the common pitfalls developers face is the inability to add empty directories directly. This limitation can hinder project organization, especially when certain folders are required for the architecture of your application. By learning the best practices for using "git add empty folder," you can become more proficient in managing your Git repositories.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will answer some frequently asked questions, provide practical examples, and share insights that can enhance your Git experience. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned developer, understanding the nuances of empty folders in Git can significantly improve your project management skills and ensure that your repository remains well-structured.
Read also:Unleash The Thrill Sun Ski Sports For Ultimate Adventure
What is the Purpose of Empty Folders in Git?
Empty folders can serve various purposes in a project. Here are a few reasons why you might want to include them:
- Organizational structure: They help maintain a clear directory hierarchy.
- Future file placement: You may plan to add files to them later.
- Documentation: They can indicate where specific components will reside.
How Does Git Handle Empty Directories?
Git is designed to track changes to files rather than directories themselves. This means that when a directory is empty, Git does not add it to the repository. Here's how Git generally handles directories:
- Only tracks files: If there are no files in a directory, it won't appear in the version control.
- Uses the .gitkeep file: A common workaround is to use a placeholder file.
- Follows file tracking: Any directory with files will be tracked normally.
How Can You Add an Empty Folder in Git?
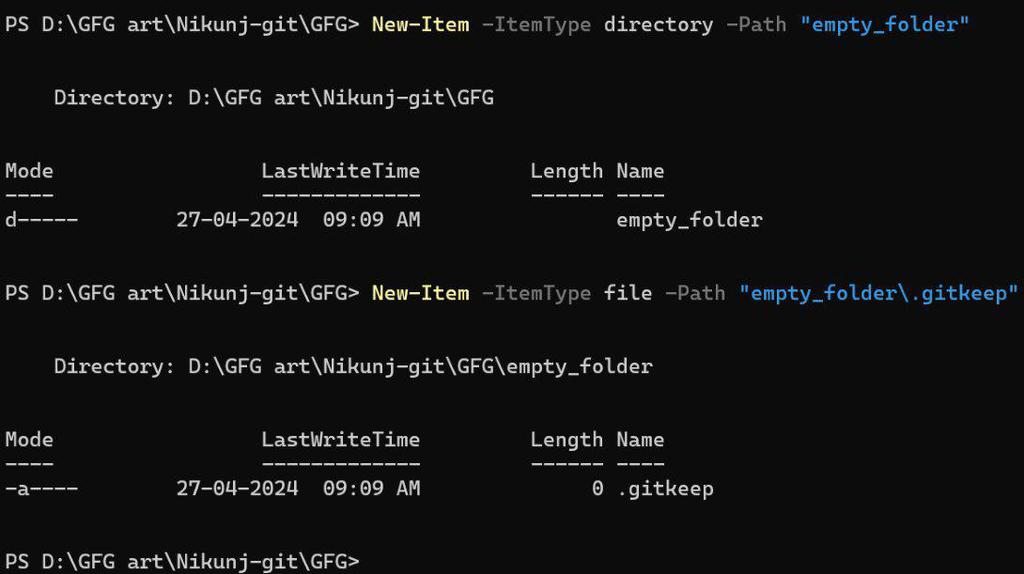
To add an empty folder in Git, you need to create a file within that folder. The most common approach is to use a hidden file like .gitkeep. Here’s how to do it:
- Create the directory: Use the command
mkdir my_empty_folder. - Navigate to the directory:
cd my_empty_folder. - Create a .gitkeep file:
touch .gitkeep. - Add the folder to Git:
git add my_empty_folder.
What is a .gitkeep File?
The .gitkeep file is a convention used by developers to ensure that empty directories are included in the Git repository. It is a simple, empty file that serves no purpose other than to signal to Git that the directory should be tracked. Here are some points to remember:
- The .gitkeep file can be named anything; its main function is to prevent the directory from being ignored by Git.
- It can be combined with other files to manage project structures efficiently.
Can You Use Other File Types to Keep Empty Folders?
Yes, while .gitkeep is the most common choice, you can use any file, such as README.md or .gitignore, to achieve the same effect. The goal is to ensure that the directory is not empty so that Git recognizes it. Consider these options:
- README.md: Provides documentation for the directory's purpose.
- .gitignore: Can be used to specify which files should be ignored in that directory.
What Happens to Empty Folders When Cloning a Repository?
When you clone a repository, only the directories with at least one file will be created. Therefore, any empty folders without a placeholder file will not be included in the cloned repository. This can lead to missing directory structures if not handled properly, so always ensure that you have a .gitkeep or similar file in your empty folders.
Read also:Meet Taylor Swifts Potential Future Boyfriend In 2024
How Can You Remove an Empty Folder from Git?
If you want to remove an empty folder from your Git repository, you can do so with the following steps:
- Delete the placeholder file (e.g., .gitkeep):
rm my_empty_folder/.gitkeep. - Remove the folder itself:
rmdir my_empty_folder. - Commit the changes:
git commit -m "Removed empty folder".
Conclusion: The Importance of Managing Empty Folders in Git
Understanding how to use "git add empty folder" correctly is crucial for maintaining an organized project structure. By using placeholder files like .gitkeep, developers can ensure that their directory hierarchies remain intact, even when some folders are empty. This practice enhances collaboration among team members and simplifies the management of complex projects.
As Git continues to be an essential tool for developers, mastering its nuances, including how to handle empty folders, will ultimately lead to a more efficient workflow. Embrace the power of Git and take control of your project organization today!
Article Recommendations