Understanding The Conversion Of Farad To Joules
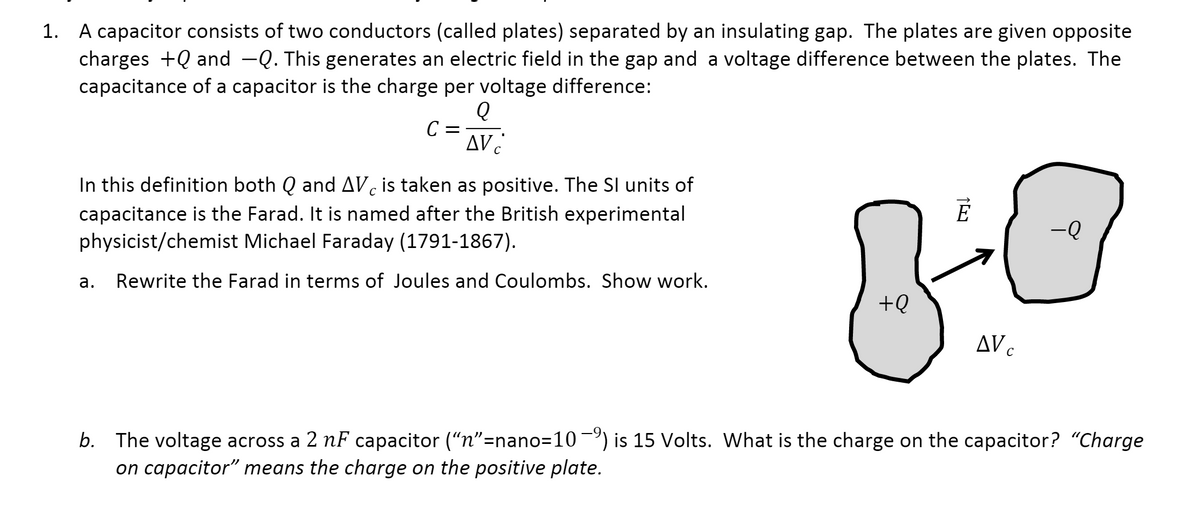
In the realm of physics and electrical engineering, units of measurement play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of electrical systems. Among these units, the farad and the joule are essential for describing capacitance and energy, respectively. The farad, a unit of capacitance, measures a component's ability to store electrical charge, while the joule quantifies the amount of energy transferred or converted in an electrical system. Understanding how to convert farads to joules can provide valuable insights into electrical circuits and the performance of various electronic devices.
For professionals working with capacitors, knowing the relationship between farads and joules is vital for designing efficient circuits. This conversion allows engineers to predict energy storage capabilities and optimize circuit performance. Moreover, it helps in troubleshooting and enhancing the functionality of electrical systems. By grasping the concept of farad to joules conversion, one can gain a deeper appreciation of electrical energy dynamics in capacitive components.
As we delve further into the topic, we will explore the formula for converting farads to joules, the significance of each unit, and practical applications of this conversion in real-world scenarios. Additionally, we will answer common questions related to energy storage and capacitance, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these two units interact in electrical systems.
Read also:Unveil Your Adventure With Taylor Swift Explore The Ultimate Tour Schedule
What is a Farad?
The farad (F) is the SI unit of capacitance, named after the renowned scientist Michael Faraday. It defines the amount of electric charge stored per unit voltage. Essentially, one farad is equivalent to storing one coulomb of charge at one volt. Capacitors, which store electrical energy, are often rated in farads, with larger capacitors capable of storing significantly more energy.
What is a Joule?
The joule (J) is the SI unit of energy, named after the physicist James Prescott Joule. It represents the amount of energy transferred when one coulomb of electric charge passes through an electric potential difference of one volt. In simpler terms, it measures the work done by a force acting over a distance. Understanding joules is crucial for evaluating the energy consumption and efficiency of electrical devices.
How are Farads and Joules Related?
The relationship between farads and joules is established through the formula for energy stored in a capacitor. The energy (E) in joules stored in a capacitor can be calculated using the formula:
E = 0.5 * C * V^2
Where:
- E = energy in joules
- C = capacitance in farads
- V = voltage in volts
This formula highlights how a capacitor's energy storage capability is influenced by both its capacitance and the voltage applied across it.
Read also:Exploring The World Of Cute Cars A Delightful Journey Into Adorable Automobile Designs
How to Convert Farads to Joules?
To convert farads to joules, one needs to know the voltage applied to the capacitor. By applying the aforementioned formula, you can calculate the energy stored in joules. For instance, if a capacitor has a capacitance of 2 farads and is charged to a voltage of 5 volts, the stored energy can be calculated as follows:
E = 0.5 * 2 * (5^2) = 0.5 * 2 * 25 = 25 joules
Why is the Conversion Important?
The conversion from farads to joules is crucial for several reasons:
- Energy Efficiency: Understanding how much energy a capacitor can store helps in designing energy-efficient systems.
- Component Selection: Engineers can select appropriate capacitors based on the energy requirements of a circuit.
- System Stability: Knowledge of energy storage capabilities aids in maintaining system stability during sudden voltage changes.
What are the Applications of Farad to Joules Conversion?
The conversion of farads to joules has various practical applications, including:
- Power Supply Design: Designing power supplies that require specific energy storage capabilities.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Optimizing energy storage in solar and wind energy systems.
- Electronic Devices: Enhancing the performance of electronic devices that rely on capacitors for energy storage.
Common Misconceptions about Farads and Joules
There are several misconceptions surrounding farads and joules, including:
- Farads Measure Energy: Many people mistakenly believe that farads directly measure energy, when they actually measure capacitance.
- Higher Capacitance Equals More Energy: While higher capacitance can store more energy, the voltage across the capacitor is equally important.
- Capacitance is Constant: Capacitance can change based on factors like voltage, temperature, and frequency.
Conclusion: Mastering Farad to Joules Conversion
In conclusion, understanding how to convert farads to joules is essential for anyone involved in electrical engineering or electronics. By grasping the relationship between capacitance and energy, one can design better circuits, optimize energy storage, and improve the overall performance of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, the importance of these conversions will only grow, making it crucial for professionals to master this knowledge.
Article Recommendations