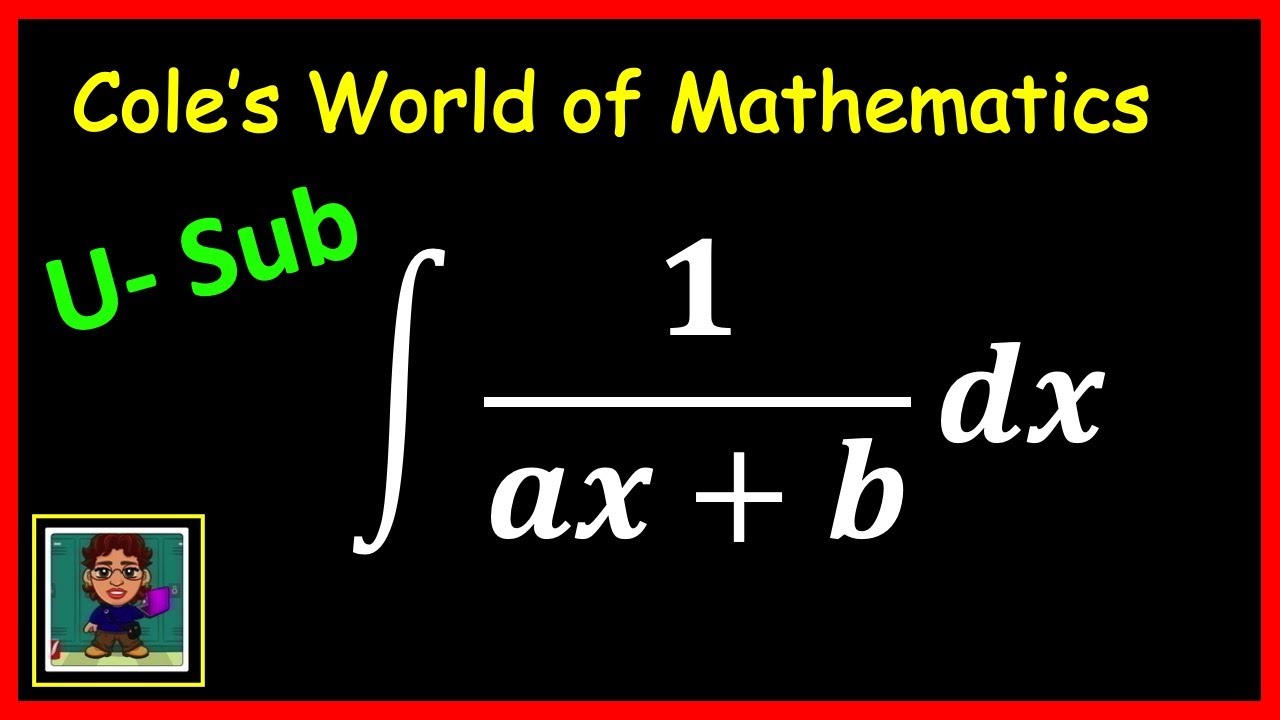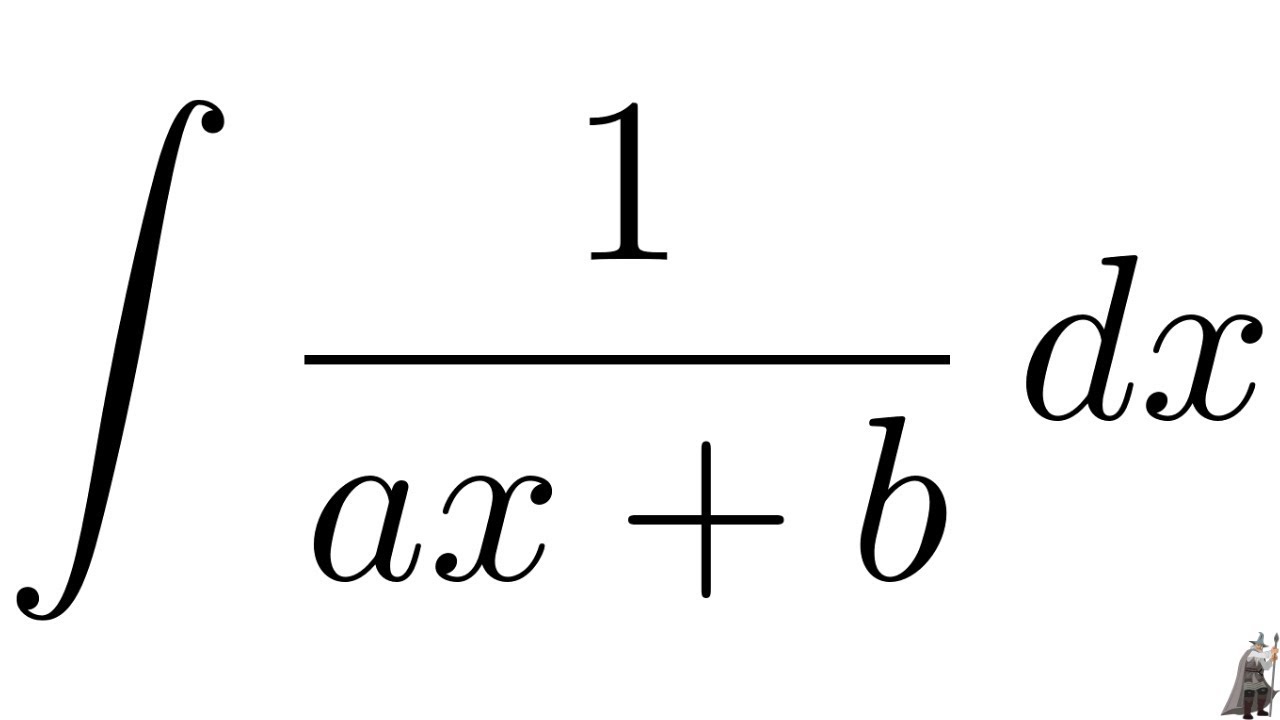Understanding The Integral Of 1 Ax B: A Comprehensive Guide
The concept of integrals is one of the cornerstones of calculus, and it plays a crucial role in various fields of mathematics and science. Among these integral calculations, the integral of 1 ax b stands out due to its simplicity and its application in solving numerous problems. This integral can be encountered in various mathematical contexts, particularly in determining the area under a curve or in solving differential equations. The beauty of this integral lies in its straightforward nature, which allows both students and professionals to grasp its significance quickly.
In this article, we will explore the integral of 1 ax b in detail, breaking down its components and understanding how to compute it effectively. By examining its properties, applications, and solving relevant examples, we aim to provide a comprehensive resource that demystifies this foundational concept. Whether you are a student preparing for exams or a professional brushing up on your calculus skills, this guide will serve as a valuable reference.
As we navigate through the intricacies of the integral of 1 ax b, we will address common questions and misconceptions surrounding the topic. Our goal is to make this complex subject matter accessible and enjoyable, ensuring that you leave with a solid understanding of integrals and their applications. So, let’s dive in and unlock the mysteries of the integral of 1 ax b!
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Lord Of The Lost An Indepth Analysis
What is the Integral of 1 ax b?
The integral of 1 ax b can be expressed mathematically as follows:
∫(1/(ax+b)) dx
This expression represents the area under the curve defined by the function 1/(ax+b). The parameters 'a' and 'b' are constants, and 'x' is the variable of integration. The integral is crucial in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics, where it can be used to calculate quantities like displacement, area, or total cost.
How Do We Compute the Integral of 1 ax b?
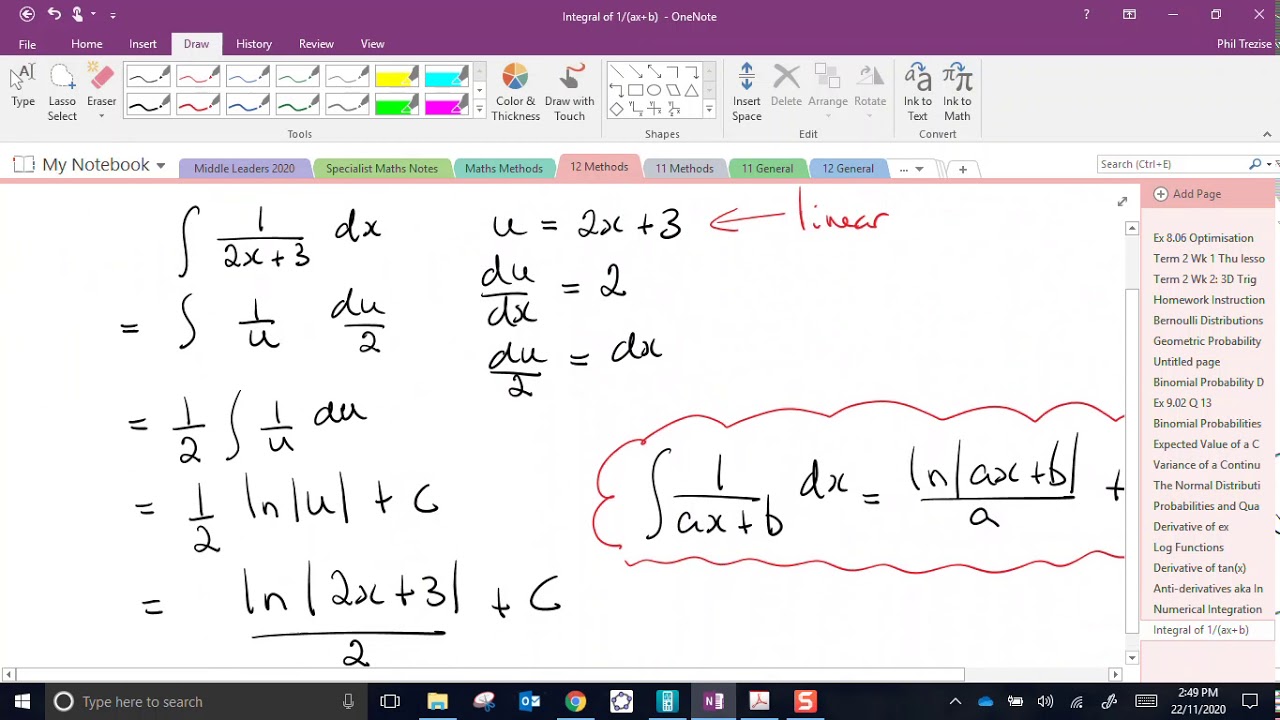
To compute the integral of 1 ax b, we can use a basic formula based on the properties of logarithmic functions. The integral can be calculated as follows:
∫(1/(ax+b)) dx = (1/a) * ln|ax+b| + C
Where 'C' is the constant of integration. This formula provides the antiderivative of the function, allowing us to find the area under the curve between specified limits.
Read also:Varsity National Yearbook Week Celebrating The Legacy And Future Of School Spirit
What Are the Steps to Solve the Integral of 1 ax b?
To solve the integral of 1 ax b, follow these steps:
- Identify the constants 'a' and 'b' in the integral.
- Apply the integral formula: ∫(1/(ax+b)) dx = (1/a) * ln|ax+b| + C.
- If limits are provided, evaluate the definite integral by substituting the limits into the antiderivative.
What Are Some Applications of the Integral of 1 ax b?
The integral of 1 ax b has several applications across various domains. Some notable applications include:
- Physics: Calculating displacement and work done in mechanics.
- Economics: Determining consumer surplus and producer surplus.
- Engineering: Analyzing signals and systems in control theory.
- Statistics: Finding cumulative distribution functions.
Can We Visualize the Integral of 1 ax b?
Visualizing the integral of 1 ax b can enhance our understanding of its geometric interpretation. The graph of the function 1/(ax+b) is a hyperbola, and the integral represents the area between this curve and the x-axis over a specified interval. By plotting the function and shading the area under the curve, we can gain insight into how the integral reflects the accumulation of area.
What Challenges Might We Encounter When Working with the Integral of 1 ax b?
While the integral of 1 ax b is relatively straightforward, several challenges may arise:
- Complex Constants: If 'a' or 'b' are complex numbers, computations may become intricate.
- Definite Integrals: Evaluating definite integrals can sometimes yield unexpected results if limits are not correctly applied.
- Integration Techniques: In more advanced scenarios, integration techniques such as substitution may be required.
What Resources Are Available for Further Learning?
For those eager to delve deeper into the world of integrals and calculus, numerous resources are available:
- Textbooks: Standard calculus textbooks often provide comprehensive explanations and practice problems.
- Online Courses: Educational platforms offer courses specifically focused on calculus and integrals.
- Tutoring: Engaging a tutor can provide personalized guidance and support.
Conclusion: Mastering the Integral of 1 ax b
In conclusion, the integral of 1 ax b serves as a fundamental concept in calculus, with wide-ranging applications across various fields. By understanding its computation, visual representation, and practical uses, students and professionals alike can enhance their mathematical prowess. Whether you are tackling this integral for the first time or revisiting it, the knowledge gained will undoubtedly prove beneficial in your academic and professional journey. Embrace the challenge, and let the integral of 1 ax b become a powerful tool in your mathematical toolkit!
Article Recommendations