Understanding RStudio Standard Deviation For Data Analysis
When diving into the world of data analysis, understanding statistical concepts is paramount. One such concept is the standard deviation, a measure that quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of data values. In the context of RStudio, a powerful statistical computing environment, the standard deviation becomes a critical tool for data scientists and analysts alike. By mastering how to calculate and interpret standard deviation using RStudio, one can gain deeper insights into data sets, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
The significance of the standard deviation lies in its ability to provide a clear picture of how spread out the values in a dataset are. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean, whereas a high standard deviation signifies that the values are spread out over a wider range. For users of RStudio, understanding how to manipulate and visualize standard deviation is crucial for effective data analysis. This guide aims to explore the basics of standard deviation within RStudio, including its calculation, interpretation, and applications.
Whether you are a seasoned data analyst or a beginner, familiarizing yourself with the RStudio standard deviation can enhance your analytical skills. It not only helps in understanding data behavior but also aids in making informed decisions based on statistical evidence. This article will walk you through various aspects of standard deviation in RStudio, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of this important statistical measure.
Read also:The Intriguing World Of Mc Meaning Unraveling The Mystery
What is Standard Deviation?
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that represents the amount of variation or dispersion in a dataset. It provides insights into how much individual data points differ from the mean (average) of the dataset. In simpler terms, it helps to identify whether the data points tend to be close to the mean or if they are widely spread out.
How is Standard Deviation Calculated in RStudio?
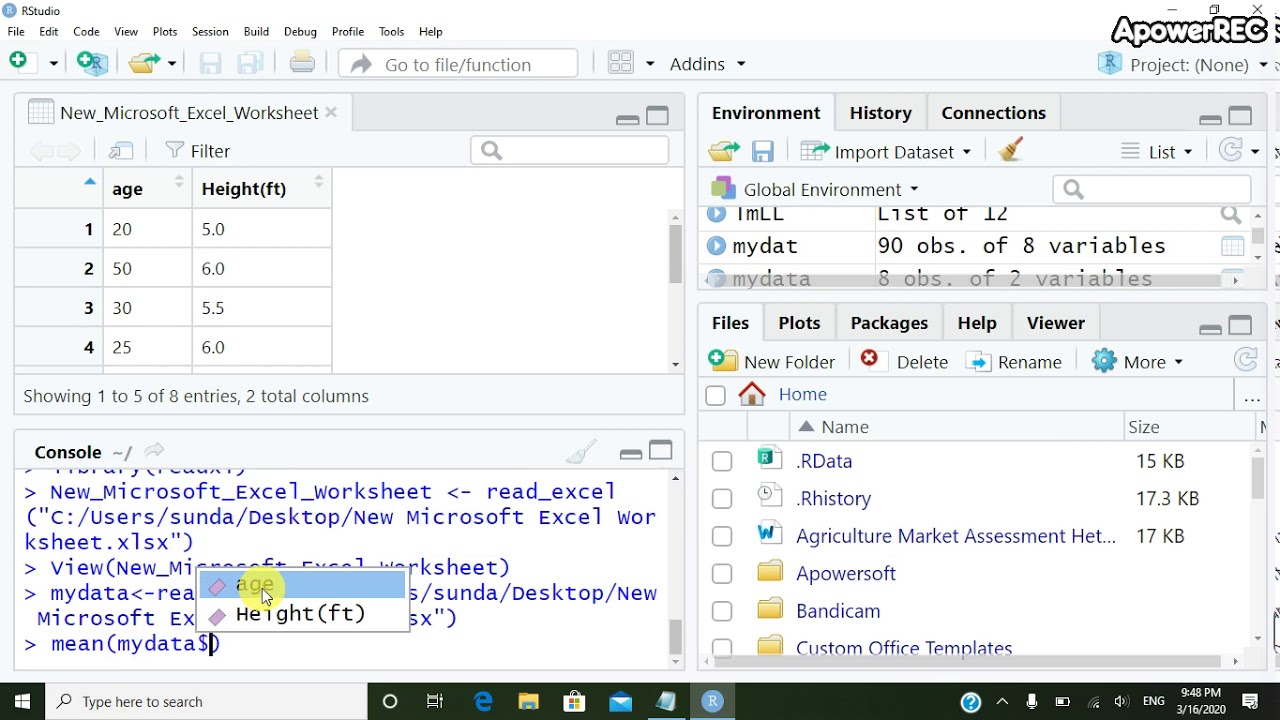
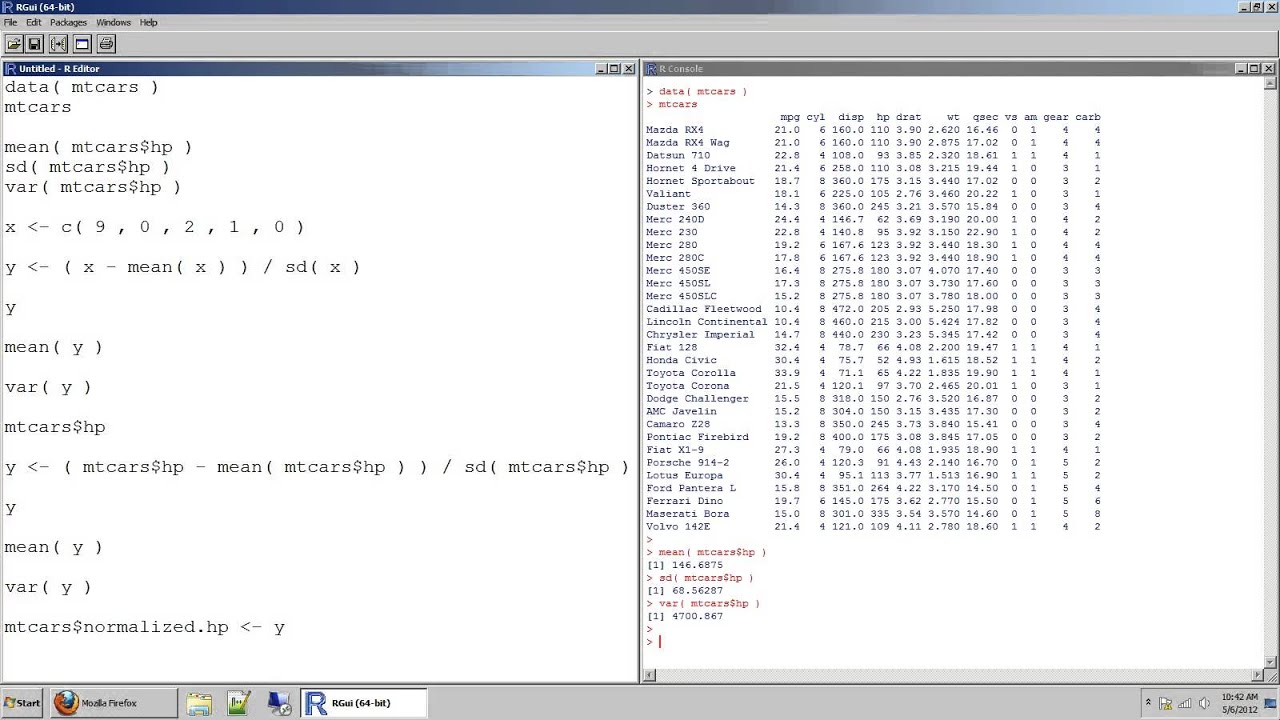
Calculating standard deviation in RStudio is straightforward. You can use the built-in function 'sd()' to compute the standard deviation of a numeric vector. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Load your dataset into RStudio.
- Use the 'sd()' function to calculate the standard deviation of a specific column or vector.
- Interpret the results to understand the data dispersion.
For example, if you have a dataset called 'data' and you want to calculate the standard deviation of the column 'scores', you would use: sd(data$scores).
What Are the Applications of Standard Deviation in Data Analysis?
Standard deviation has several applications in data analysis, including:
- Identifying variability within data sets.
- Comparing the spread of different datasets.
- Making predictions based on historical data.
- Conducting hypothesis testing.
By applying standard deviation, analysts can better understand the underlying patterns and trends in their data.
What are the Limitations of Standard Deviation?
Despite its usefulness, standard deviation has certain limitations:
Read also:Long Island Jewish Hospital A Comprehensive Overview Of Excellence In Healthcare
- It is sensitive to outliers, which can skew results.
- It assumes a normal distribution of data, which may not always be the case.
- It does not provide information about the shape of the distribution.
Being aware of these limitations is essential for accurate data interpretation.
How Can Visualizations Enhance Understanding of Standard Deviation?
Visualizations play a crucial role in data analysis, especially when it comes to understanding standard deviation. Graphical representations such as:
- Box plots
- Histograms
- Scatter plots
can help analysts visualize the spread and distribution of data, making it easier to identify patterns and anomalies. RStudio offers various packages, such as ggplot2, that facilitate the creation of these visualizations.
How to Interpret Standard Deviation Results in RStudio?
Interpreting standard deviation results requires a basic understanding of what the values signify:
- A standard deviation close to zero indicates that the data points are clustered around the mean.
- A higher standard deviation suggests a wider range of values and greater variability.
- Positive and negative standard deviations indicate how far the data points deviate from the mean in both directions.
By interpreting these results, analysts can draw meaningful conclusions about their datasets.
Conclusion: Mastering RStudio Standard Deviation for Effective Data Analysis
Understanding and applying standard deviation in RStudio is essential for anyone involved in data analysis. By mastering this concept, analysts can gain insights into data variability, enhance their analytical skills, and make informed decisions based on statistical evidence. Whether you're calculating standard deviation for a simple dataset or using it in complex analyses, RStudio provides the tools needed to effectively manipulate and visualize this important statistical measure.
Article Recommendations