Understanding The Dynamics Of Host Vs Client Computer
In the realm of computer networking, the terms "host" and "client" hold significant importance. These two concepts form the backbone of communication between devices, whether in a local network or across the internet. Understanding the host vs client computer relationship is crucial for anyone interested in computer science, network administration, or IT services. As technology advances, the interaction between host and client computers becomes increasingly complex, yet essential for efficient data transmission and resource sharing.
Host computers serve as the central point of a network, providing resources and services to client computers. Clients, on the other hand, are devices that request and utilize these services. This dynamic creates a symbiotic relationship that is fundamental to modern computing. With the rise of cloud computing, mobile devices, and IoT (Internet of Things), the host-client model is evolving, reshaping the way we think about computing infrastructure.
In this article, we will explore various aspects of host vs client computers, examining their functions, characteristics, and differences. By the end of this discussion, readers will have a clearer understanding of how these two components interact and the implications for network design and management.
Read also:How To Make Stickers A Comprehensive Guide
What is a Host Computer?
A host computer is any computer that provides data, services, or resources to other computers, known as clients. In a typical network setup, a host can be a server, a desktop, or even a specialized device like a printer. The primary role of a host computer includes:
- Storing and managing data
- Running applications that can be accessed by clients
- Facilitating communication between different devices on the network
- Providing shared resources, such as files or printers
What is a Client Computer?
Client computers are devices that access services and resources provided by host computers. These can include personal computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The main functions of client computers are:
- Sending requests to the host for data or services
- Receiving and displaying information from the host
- Running client-side applications that interact with the host
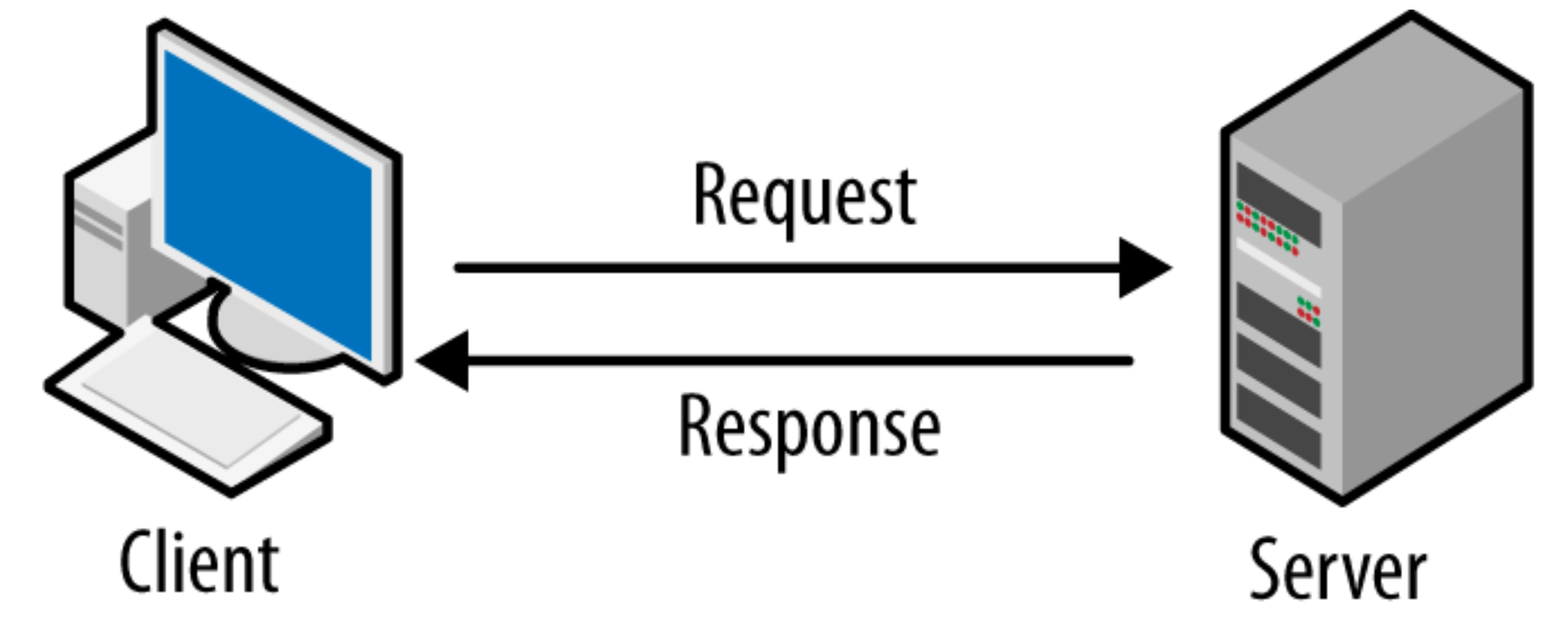
How Does the Host vs Client Computer Relationship Work?
In a network environment, the interaction between host and client computers is governed by a set of protocols that dictate how requests and responses are handled. Here’s a simplified process of their interaction:
- The client sends a request to the host.
- The host processes the request and retrieves the necessary data or service.
- The host sends the response back to the client.
- The client receives and processes the information, displaying it to the user.
What are the Key Differences Between Host and Client Computers?
Understanding the differences between host and client computers is essential for network design and management. Here are some of the key distinctions:
| Feature | Host Computer | Client Computer |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides services and resources | Requests and uses services |
| Processing Power | Generally more powerful with greater resources | Often less powerful, designed for specific tasks |
| Network Responsibility | Manages network resources | Utilizes network resources |
| Examples | Servers, mainframes | PCs, laptops, tablets |
How is the Host vs Client Computer Model Applied in Real Life?
The host vs client computer model is prevalent in various applications and services we use daily. Some practical examples include:
- Web Browsing: The web server acts as a host, while your browser is the client.
- Email: An email server hosts your emails, and your email client retrieves them.
- File Sharing: A file server hosts files, and client computers access those files over the network.
Why is Understanding Host vs Client Computers Important for Networking?
Comprehending the dynamics of host vs client computers is vital for several reasons:
Read also:The Legacy And Impact Of The Black Panther Party A Comprehensive Examination
- Effective network design: Knowing how hosts and clients interact helps in creating efficient networks.
- Troubleshooting: Understanding the roles of host and client can aid in diagnosing network issues.
- Resource Allocation: Proper management of hosts ensures optimal performance for clients.
How Does the Evolution of Technology Impact Host vs Client Computers?
With the rapid advancement of technology, the host vs client computer model is constantly evolving. Here are some trends that are reshaping this dynamic:
- Cloud Computing: Many applications now run on cloud servers, changing the traditional host-client interaction.
- Mobile Devices: Increased use of smartphones and tablets as clients has shifted how services are delivered.
- IoT Devices: The rise of IoT has introduced multiple clients that communicate with a variety of hosts.
What Future Trends Can We Expect in Host vs Client Computing?
As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate several trends in the host vs client computer relationship:
- Increased reliance on edge computing, where processing occurs closer to the client devices.
- More decentralized systems, reducing the reliance on traditional host models.
- Enhanced security measures to protect data shared between hosts and clients.
Conclusion: The Importance of the Host vs Client Computer Model
The host vs client computer model is a fundamental aspect of networking that underpins much of our digital interactions today. Understanding this relationship is crucial for anyone involved in IT, networking, or computer science. As technology evolves, so does the interaction between hosts and clients, creating new opportunities and challenges. By grasping these concepts, individuals and organizations can better navigate the complexities of modern computing and network management.
Article Recommendations