Understanding The Extrinsic And Intrinsic Semiconductor Difference
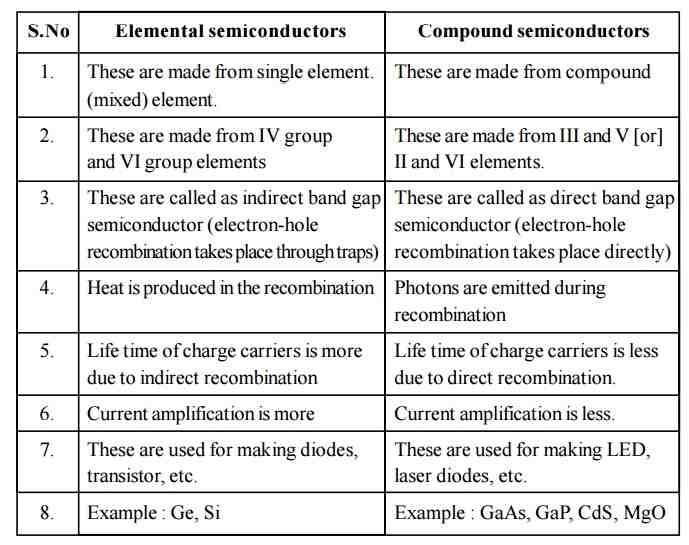
In the realm of electronics and technology, semiconductors play a pivotal role in the functioning of various devices. Understanding the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic semiconductors is crucial for anyone delving into the field of electronics. Intrinsic semiconductors refer to pure semiconductor materials, while extrinsic semiconductors are those that have been doped with impurities to enhance their electrical properties. This distinction lays the foundation for much of modern electronic circuitry, making it essential for engineers and enthusiasts alike to grasp these concepts.
The properties of semiconductors are influenced by the arrangement of their atoms and the presence of impurities. Intrinsic semiconductors consist of a perfect crystal lattice structure, where the number of charge carriers is determined solely by temperature. On the other hand, extrinsic semiconductors have been intentionally altered to improve their conductivity by adding specific dopants. This enhancement is vital for creating components like diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits, which are ubiquitous in modern technology.
As technology continues to advance, the demand for efficient and effective semiconductor materials grows. Recognizing the extrinsic and intrinsic semiconductor difference not only aids in understanding how these materials function but also highlights their applications in various electronic devices. This article seeks to explore these differences in detail, answering common questions and shedding light on the significance of each type of semiconductor.
Read also:Exploring The Best Cheap Motels In Las Vegas For A Budgetfriendly Stay
What is an Intrinsic Semiconductor?
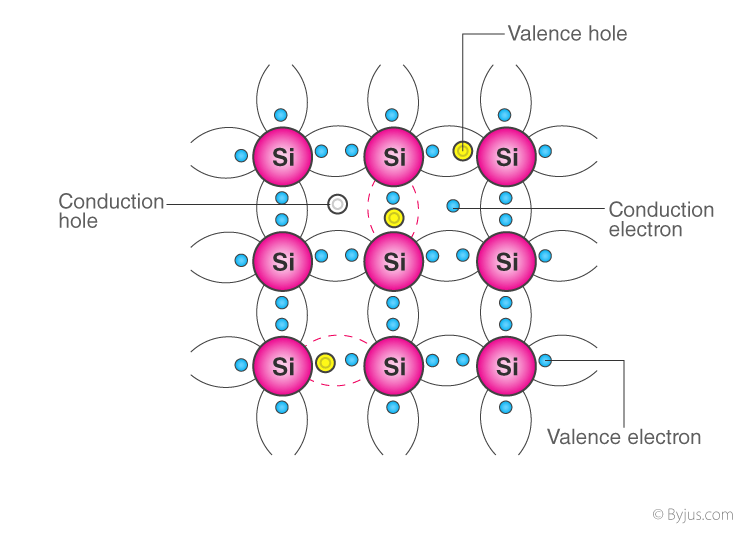
Intrinsic semiconductors are materials that are pure and not intentionally doped with impurities. The most common examples include silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge). These materials have a balanced number of electrons and holes, allowing them to conduct electricity under certain conditions.
Characteristics of Intrinsic Semiconductors
- High purity levels without any dopants.
- Conductivity increases with temperature due to the generation of electron-hole pairs.
- Typically have a lower conductivity compared to extrinsic semiconductors.
- Used in applications requiring minimal interference from impurities.
Applications of Intrinsic Semiconductors
Intrinsic semiconductors are primarily used in applications where high purity is essential, such as:
- Photovoltaic cells.
- High-temperature sensors.
- Optoelectronic devices.
What is an Extrinsic Semiconductor?
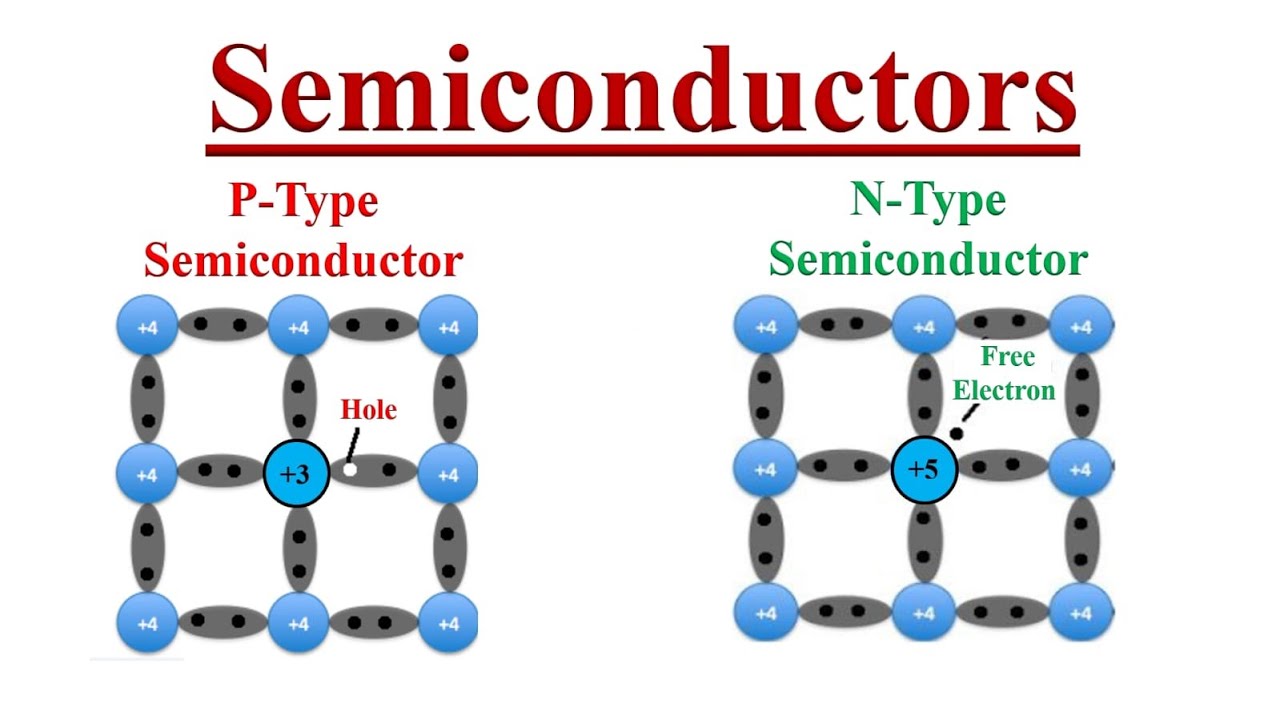
Extrinsic semiconductors are those that have been intentionally doped with impurities to enhance their electrical properties. The doping process introduces additional charge carriers, which significantly increases the material's conductivity. The two main types of extrinsic semiconductors are n-type and p-type.
Characteristics of Extrinsic Semiconductors
- Enhanced conductivity compared to intrinsic semiconductors.
- Can be tailored for specific electrical properties by choosing appropriate dopants.
- Consist of either excess electrons (n-type) or holes (p-type).
- Widely used in electronic devices due to their superior performance.
Applications of Extrinsic Semiconductors
Extrinsic semiconductors are utilized in a variety of electronic components, such as:
- Transistors.
- Diodes.
- Integrated circuits.
- LEDs and laser diodes.
How Do Extrinsic and Intrinsic Semiconductors Differ in Conductivity?
The primary difference in conductivity between extrinsic and intrinsic semiconductors lies in the presence of dopants. While intrinsic semiconductors rely on thermal energy to generate charge carriers, extrinsic semiconductors have an abundance of free charge carriers due to doping. This results in a significantly higher conductivity in extrinsic materials.
What Role Do Temperature and Doping Play?
Temperature and doping are critical factors influencing the performance of semiconductors. In intrinsic semiconductors, rising temperatures lead to increased charge carrier generation. In contrast, extrinsic semiconductors maintain high conductivity at lower temperatures due to the presence of dopants, which provide additional charge carriers.
Read also:Shop Harbor Freight For Bestselling Tools And Equipment
What Are the Advantages of Using Extrinsic Semiconductors Over Intrinsic Semiconductors?
Extrinsic semiconductors offer several advantages over their intrinsic counterparts:
- Higher conductivity, making them suitable for various applications in electronics.
- Ability to customize electrical properties by selecting specific dopants.
- Improved performance in devices requiring rapid switching and amplification.
- Widespread use in modern electronic components, enhancing overall device efficiency.
What Are the Limitations of Extrinsic Semiconductors?
Despite their advantages, extrinsic semiconductors also have limitations:
- Possible degradation of performance due to increased temperature.
- Dependence on the quality and concentration of dopants used.
- Potential for reduced stability and reliability in certain applications.
Conclusion: Why Understanding the Extrinsic and Intrinsic Semiconductor Difference Matters?
Grasping the extrinsic and intrinsic semiconductor difference is essential for anyone involved in electronics and technology. These concepts lay the groundwork for understanding how semiconductors function, their applications, and their importance in modern devices. As technology continues to evolve, the role of semiconductors will only grow, making this knowledge increasingly relevant.
In summary, intrinsic semiconductors provide a foundation of pure materials, while extrinsic semiconductors enhance conductivity through doping. Recognizing the differences between these two types of semiconductors is crucial for developing efficient electronic components and advancing future technologies.
Article Recommendations