Understanding 37 Hydrochloric Acid Molarity: A Comprehensive Guide
The chemical world is full of intriguing compounds, and hydrochloric acid (HCl) stands out as an essential substance in various industrial and laboratory settings. One of the most concentrated forms of this acid is the 37% hydrochloric acid solution, commonly used due to its strong acidic properties. Understanding the molarity of such a solution is crucial for chemists and professionals who work with this powerful reagent. Molarity, defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution, helps in determining the exact concentration and potential reactivity of the acid.
When working with 37 hydrochloric acid molarity, it’s essential to grasp not only the chemical properties of hydrochloric acid but also its applications and the safety measures required to handle it. This article delves into the intricacies of hydrochloric acid, including its concentration, molarity calculations, and various applications in different fields. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of how to work with this potent acid safely and effectively.
As we explore further, we will answer some critical questions surrounding 37 hydrochloric acid molarity. From its preparation to its uses in laboratories and industries, this guide will provide valuable insights for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge about this vital chemical compound. So, let’s get started!
Read also:Texas Tech Lady Raiders Basketball The Ultimate Guide
What is Hydrochloric Acid and Why is Molarity Important?
Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid composed of hydrogen and chloride ions, represented chemically as HCl. It is a colorless, corrosive liquid with a distinct pungent odor. The acid is highly soluble in water, which makes it a common choice for various applications, including:
- pH regulation in swimming pools
- Cleaning agents in industrial processes
- Food processing and preservation
- Laboratory reagent in chemical synthesis
Molarity plays a critical role in understanding the concentration of hydrochloric acid solutions. It allows chemists to make precise calculations for reactions, dilutions, and formulations, ensuring accurate and safe chemical handling.
How is 37 Hydrochloric Acid Molarity Calculated?
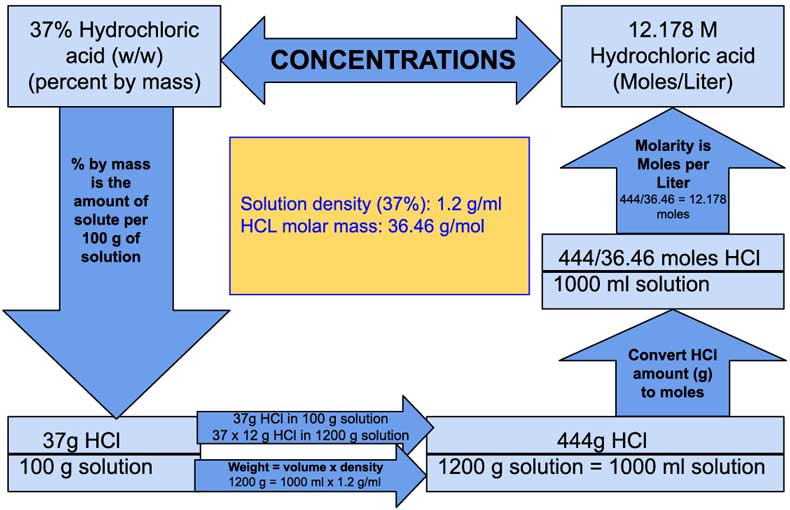
To calculate the molarity of a 37% hydrochloric acid solution, you need to know the density of the solution and the molecular weight of HCl. The steps involved in this calculation are as follows:
- Determine the density of the 37% hydrochloric acid solution (approximately 1.19 g/mL).
- Calculate the mass of HCl in 1 liter of solution.
- Convert the mass to moles using the molecular weight of HCl (approximately 36.46 g/mol).
- Calculate the molarity using the formula: Molarity (M) = moles of solute / liters of solution.
By following these steps, you can find that the molarity of a 37% hydrochloric acid solution is around 12 M (moles per liter), indicating a highly concentrated acidic solution suitable for various chemical processes.
What Precautions Should Be Taken When Handling 37 Hydrochloric Acid?
Working with 37 hydrochloric acid requires stringent safety measures due to its corrosive nature. Here are some essential precautions:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
- Use the acid in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Store hydrochloric acid in a cool, dry place, away from incompatible substances.
- Be familiar with emergency procedures and have neutralizing agents available in case of spills.
What are the Applications of 37 Hydrochloric Acid Molarity in Industry?
37 hydrochloric acid molarity finds applications in various industries, including:
Read also:Unleash The Thrill Sun Ski Sports For Ultimate Adventure
- Metal cleaning and pickling to remove rust and scale.
- Production of chlorine and sodium carbonate.
- Food processing for pH adjustment in products.
- Oil well acidizing to enhance oil recovery.
These applications showcase the versatility and importance of hydrochloric acid in industrial processes.
How is 37 Hydrochloric Acid Used in Laboratories?
In laboratory settings, 37 hydrochloric acid molarity is utilized for:
- Preparing buffer solutions and reagents for various experiments.
- Performing titrations and acid-base reactions.
- Cleaning laboratory glassware due to its effective stain removal properties.
Understanding how to dilute and work with high molarity solutions is crucial for accurate lab results.
Are There Any Alternatives to 37 Hydrochloric Acid Molarity?
While 37 hydrochloric acid is widely used, alternatives exist depending on the application:
- Citric acid for food applications as a safer acid.
- Acetic acid for cleaning purposes.
- Sulfuric acid in certain industrial processes.
Choosing the right acid depends on the desired reactivity, safety considerations, and specific application requirements.
Conclusion: Mastering 37 Hydrochloric Acid Molarity
Understanding 37 hydrochloric acid molarity is essential for anyone working in chemistry-related fields. From its calculation to its safe handling and diverse applications, mastering this knowledge enhances your ability to work effectively with one of the most common acids used today. Whether in laboratories or industrial environments, being well-versed in the properties and precautions associated with hydrochloric acid is crucial for safety and success.
Article Recommendations