Exploring The Depths Of Infinite Series: Evaluating Indefinite Integrals
In the realm of calculus, the concept of evaluating indefinite integrals as an infinite series opens up a world of mathematical exploration and understanding. By utilizing infinite series, mathematicians can simplify complex integrals, making it easier to analyze functions and their behaviors. This approach not only aids in theoretical mathematics but also has practical applications in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics. Understanding how to evaluate these integrals as infinite series can provide deeper insights into the nature of functions and their integrative properties.
As we dive deeper into the process of evaluating the indefinite integral as an infinite series, we will uncover a variety of methods and techniques. From Taylor and Maclaurin series to more advanced series like Fourier series, each method has its own unique approach and utility. This article aims to demystify these concepts, providing a clear path for students and enthusiasts alike to grasp the intricacies of infinite series in relation to indefinite integrals.
Moreover, this exploration will not only enhance your mathematical toolkit but also encourage critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By learning how to effectively evaluate the indefinite integral as an infinite series, one can tackle more complex problems with confidence. So, let’s embark on this intellectual journey and uncover the beauty of calculus through the lens of infinite series.
Read also:Why Do Beavers Build Dams Unveiling The Mysteries Behind Their Ingenious Construction
What is an Indefinite Integral?
An indefinite integral, also known as an antiderivative, represents a family of functions whose derivative is the integrand. It is denoted as ∫f(x)dx and results in a function plus a constant of integration (C). Understanding indefinite integrals is crucial for exploring their evaluation as infinite series.
How Do Infinite Series Relate to Indefinite Integrals?
Infinite series are sums of infinitely many terms, and they can approximate functions to a high degree of accuracy. When evaluating the indefinite integral as an infinite series, one can express functions as a series of terms, which can then be integrated term by term. This process not only simplifies calculations but also provides deeper insights into the behavior of the function.
What are Taylor and Maclaurin Series?
Taylor and Maclaurin series are two foundational types of infinite series used to represent functions. The Taylor series expands a function around a point using its derivatives, while the Maclaurin series is a special case of the Taylor series centered around zero. These series can be incredibly useful in evaluating indefinite integrals.
How to Derive a Taylor Series?
To derive a Taylor series for a function f(x) about a point a, you can use the formula:
f(x) = f(a) + f'(a)(x-a) + f''(a)(x-a)²/2! + f'''(a)(x-a)³/3! + ...
This series allows us to express complex functions in a polynomial form, which can be easily integrated term by term.
Read also:Peoria Civic Center In Peoria Il Your Ultimate Guide
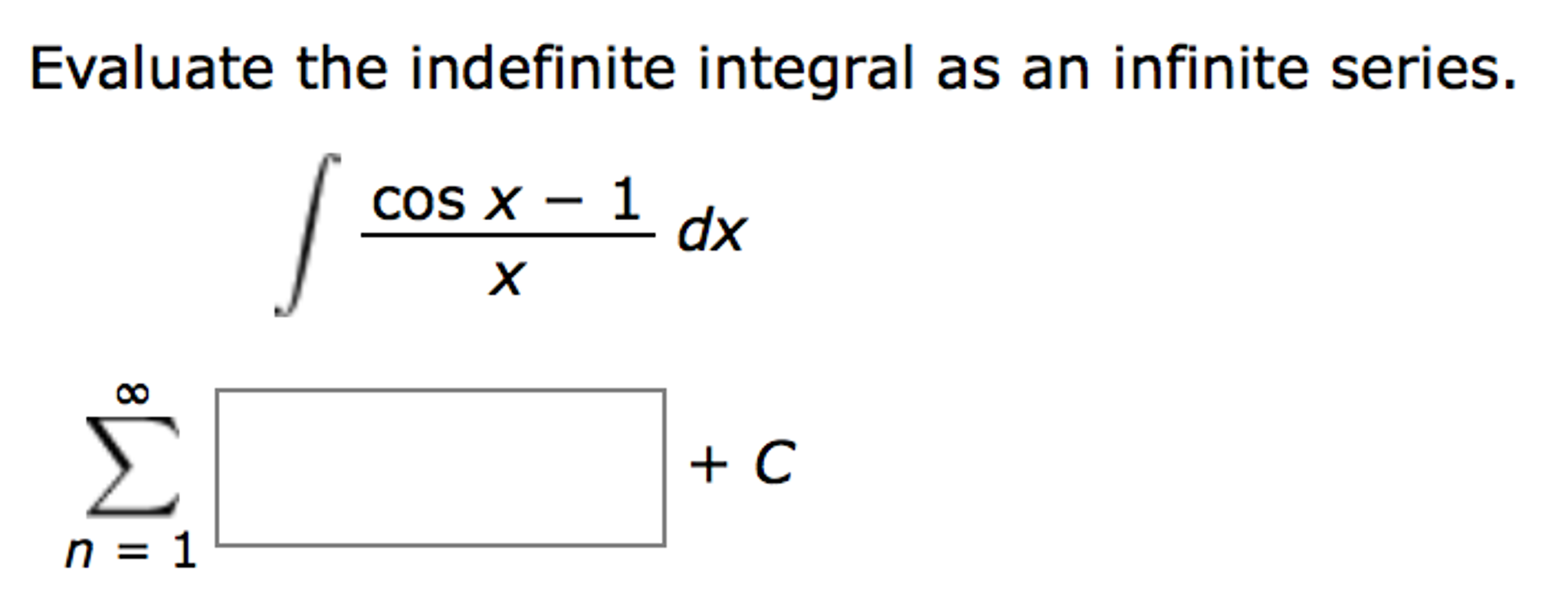
Evaluate the Indefinite Integral as an Infinite Series: Step-by-Step Guide
To evaluate the indefinite integral as an infinite series, follow these steps:
- Identify the function you wish to integrate.
- Express the function as a Taylor or Maclaurin series.
- Integrate the series term by term.
- Combine the results and include the constant of integration.
What are Fourier Series?
Fourier series allow us to represent periodic functions as sums of sines and cosines. These series are particularly useful in solving differential equations and can be applied to evaluate indefinite integrals for periodic functions.
How to Apply Fourier Series in Evaluating Indefinite Integrals?
When applying Fourier series to evaluate the indefinite integral as an infinite series, follow these steps:
- Express the periodic function as a Fourier series.
- Integrate the series term by term over one period.
- Combine the results to get the final expression.
Examples of Evaluating Indefinite Integrals as Infinite Series
Let’s look at a few examples to better understand the process:
- Evaluating the integral of e^x:
- Evaluating the integral of sin(x):
The Taylor series for e^x is:
e^x = 1 + x + x²/2! + x³/3! + ...
Integrating term by term gives:
∫e^x dx = x + x²/2 + x³/6 + ... + C
The Maclaurin series for sin(x) is:
sin(x) = x - x³/3! + x⁵/5! - ...
Integrating term by term gives:
∫sin(x) dx = -cos(x) + C
What Are the Advantages of Evaluating Indefinite Integrals as Infinite Series?
Evaluating the indefinite integral as an infinite series provides several advantages, including:
- Greater accuracy in approximating functions.
- Simplification of complex integrals.
- Deeper understanding of function behavior.
- Ability to handle a wider range of functions.
Conclusion: The Beauty of Evaluating Indefinite Integrals as Infinite Series
In conclusion, evaluating the indefinite integral as an infinite series is a powerful technique in calculus that allows for greater flexibility and understanding of functions. By mastering this technique, students and professionals alike can tackle more complex mathematical problems with confidence. The journey through infinite series not only enhances mathematical prowess but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the beauty of calculus.
Article Recommendations
![Evaluate indefinite integral as an infinite series [(e^x 1)/x]. State](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/LzQXI9aVT8A/maxresdefault.jpg)
