Understanding The Differences Between EV Charger AC Vs DC
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, understanding the different types of charging systems becomes crucial for EV owners and potential buyers. One of the primary distinctions in EV charging technology is between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) chargers. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, impacting charging times, infrastructure costs, and overall user experience. With the rise of sustainable transportation, it’s essential to grasp how these charging systems operate and their respective roles in supporting the EV ecosystem. This knowledge can help consumers make informed decisions when it comes to purchasing electric vehicles and selecting the appropriate charging solutions for their needs.
AC chargers are typically used for home charging and lower-powered charging stations, while DC chargers are designed for rapid charging at public stations. Understanding these differences can guide EV users in choosing the right charging options based on their lifestyle and driving habits. Additionally, as technology continues to evolve, the efficiency and capabilities of both AC and DC chargers are being enhanced, allowing for even faster and more convenient charging solutions.
In this article, we will explore the intricacies of EV charger AC vs DC, examining their functionalities, benefits, and limitations. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of which type of charger may best suit your electric vehicle needs, paving the way for a more seamless and efficient EV ownership experience.
Read also:Empowering Young Leaders Jslt Jackson County Student Leadership Team
What is an AC Charger?
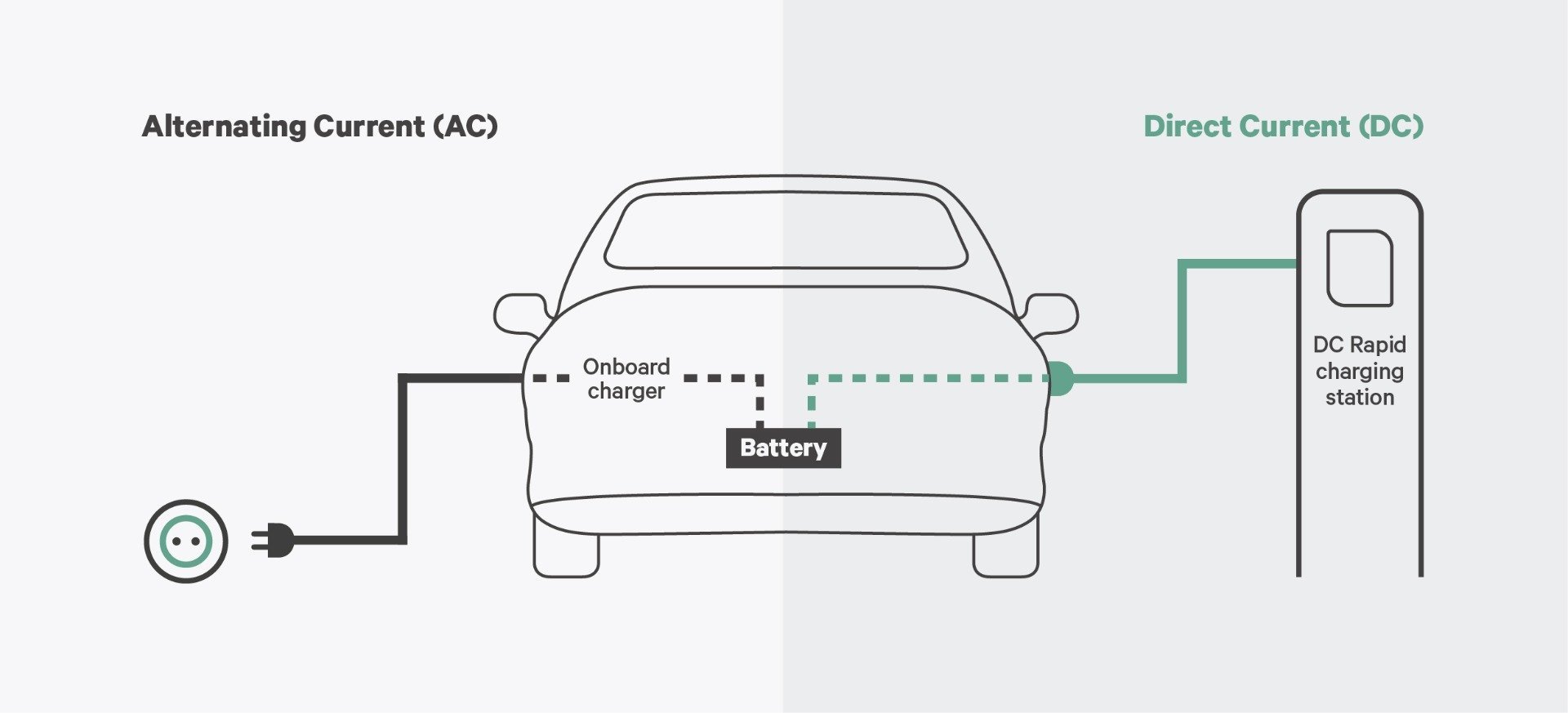
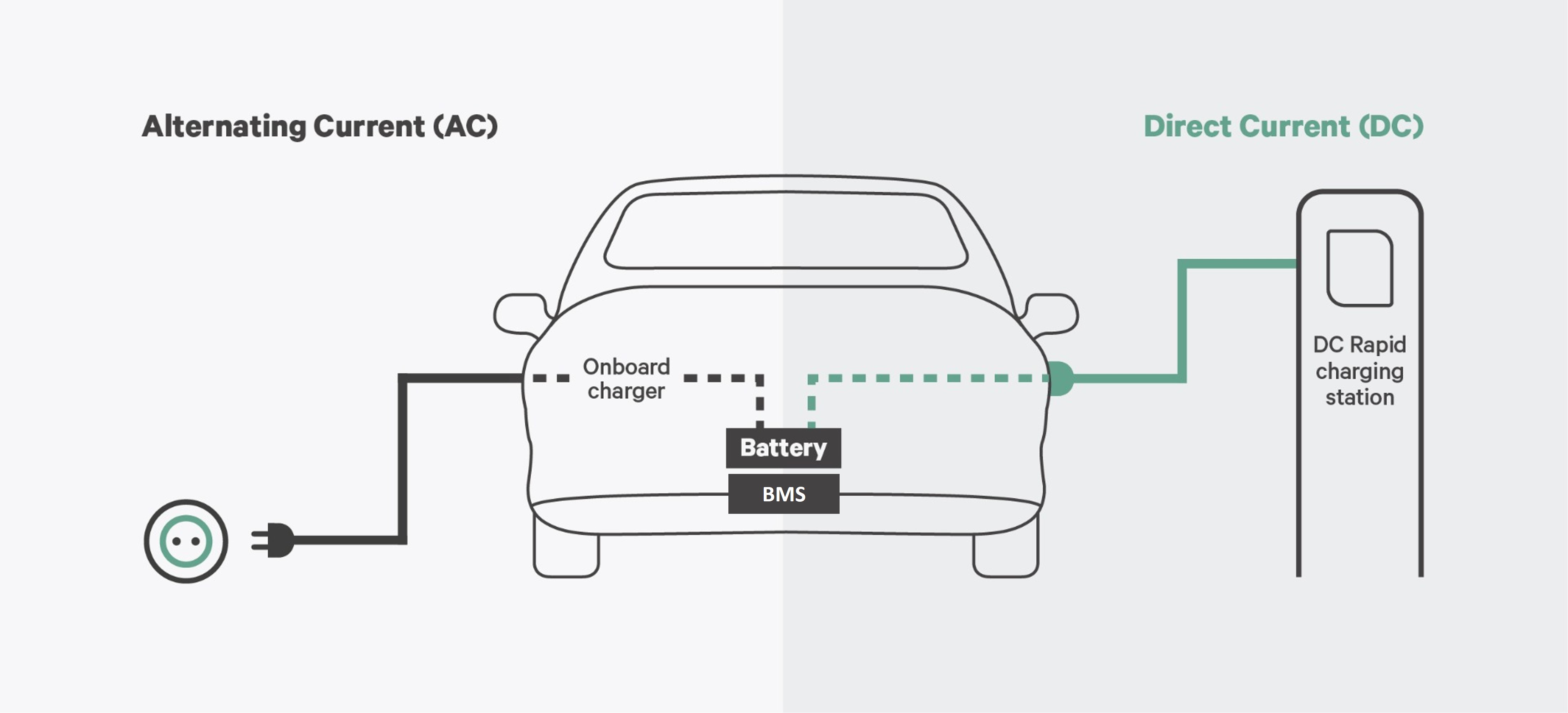
AC chargers convert electrical energy from the grid into alternating current, which is then used to charge the electric vehicle's battery. They are often found in residential settings and some public charging stations. Here are some key features of AC chargers:
- Typically, slower charging speeds compared to DC chargers.
- More common for home installations.
- Utilizes a Type 1 or Type 2 connector depending on the region.
- Usually compatible with Level 1 (120V) and Level 2 (240V) charging options.
How Does an AC Charger Work?
AC chargers operate by allowing the vehicle's onboard charger to convert AC power into DC power, which the vehicle's battery can store. The charging time can vary significantly based on the power output of the charger and the vehicle's battery capacity. Generally, AC charging is well-suited for overnight charging at home.
What is a DC Charger?
DC chargers, on the other hand, deliver direct current directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This enables much faster charging times, making it an ideal option for quick charging at public stations. Key features of DC chargers include:
- Rapid charging capabilities, often providing an 80% charge in 30 minutes or less.
- More expensive installation and infrastructure costs.
- Uses connectors such as CCS (Combined Charging System) or CHAdeMO.
- Primarily found at commercial charging stations.
How Does a DC Charger Work?
DC chargers operate by converting AC power from the grid into DC power before delivering it directly to the vehicle's battery. This eliminates the need for the vehicle's onboard charger to perform the conversion, allowing for significantly faster charging times. DC chargers are particularly beneficial for long-distance travel, where quick charging stations are necessary.
What Are the Main Differences Between EV Charger AC vs DC?
The differences between EV charger AC and DC can be summarized as follows:
- Charging Speed: DC chargers provide much faster charging times compared to AC chargers.
- Installation Cost: AC chargers are generally less expensive to install than DC chargers.
- Convenience: AC chargers are suitable for home use, while DC chargers are more common at public charging stations.
- Compatibility: Not all electric vehicles are compatible with both types of chargers, so it's essential to check your vehicle's specifications.
Which Type of Charger is Best for You?
Choosing between an AC and DC charger depends on several factors, including your driving habits, charging location, and the type of electric vehicle you own. Consider the following:
Read also:The Enigmatic Dinosaur With Spikes On Back A Journey Into The Past
- If you primarily charge at home and have a longer time to charge, an AC charger may be sufficient.
- If you frequently travel long distances and need quick charging options, a DC charger is advisable.
- Evaluate the availability of charging stations in your area, as this may influence your choice.
Are There Any Limitations to AC and DC Chargers?
Both AC and DC chargers have their limitations:
- AC Chargers: Slower charging speeds can be inconvenient for those with busy lifestyles.
- DC Chargers: Higher installation and operational costs can deter some businesses from offering these chargers.
What is the Future of EV Charging Technology?
The future of EV charging technology looks promising, with advancements in both AC and DC charging systems. Innovations such as wireless charging, ultra-fast charging stations, and improved battery technologies will likely enhance the charging experience for EV users. As electric vehicle adoption continues to rise, the infrastructure for both AC and DC chargers will need to evolve to meet demand, ensuring that charging remains convenient and efficient.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between EV charger AC vs DC is essential for anyone considering an electric vehicle. By evaluating the benefits and limitations of each type, you can make informed decisions that align with your lifestyle and driving needs. As technology continues to advance, it is clear that both AC and DC chargers will play pivotal roles in the future of sustainable transportation.
Article Recommendations
.png?width=1280&name=Understanding electricity (2).png)