Understanding The Power Factor Of RLC Circuit: A Comprehensive Guide
The power factor of RLC circuit is a crucial concept in electrical engineering that determines the efficiency of power usage in alternating current (AC) systems. A deep understanding of this concept not only helps in optimizing energy consumption but also aids in improving the performance of electrical devices. The RLC circuit, consisting of resistors (R), inductors (L), and capacitors (C), plays a significant role in various industrial and household applications. Therefore, grasping the nuances of its power factor can lead to more efficient designs and implementations.
In the world of electronics, the power factor signifies how effectively electrical power is being converted into useful work output. A power factor of 1 (or 100%) indicates that all the energy supplied is being utilized efficiently, while a power factor less than 1 signifies wasted energy. For RLC circuits, the power factor is influenced by the reactive components – inductors and capacitors – which can lead to energy losses if not managed properly. Understanding these dynamics is essential for engineers and technicians working with AC circuits.
Furthermore, the power factor of RLC circuit can significantly impact the operational costs of electrical systems. Industries are often charged higher rates for low power factors, leading to increased operational expenses. Therefore, managing and optimizing the power factor is not just a technical requirement but also a financial necessity. This article delves into the various aspects of the power factor in RLC circuits, offering insights into its significance, calculation methods, and optimization strategies.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Bisquick Biscuits A Delicious Journey
What is the Power Factor in RLC Circuits?
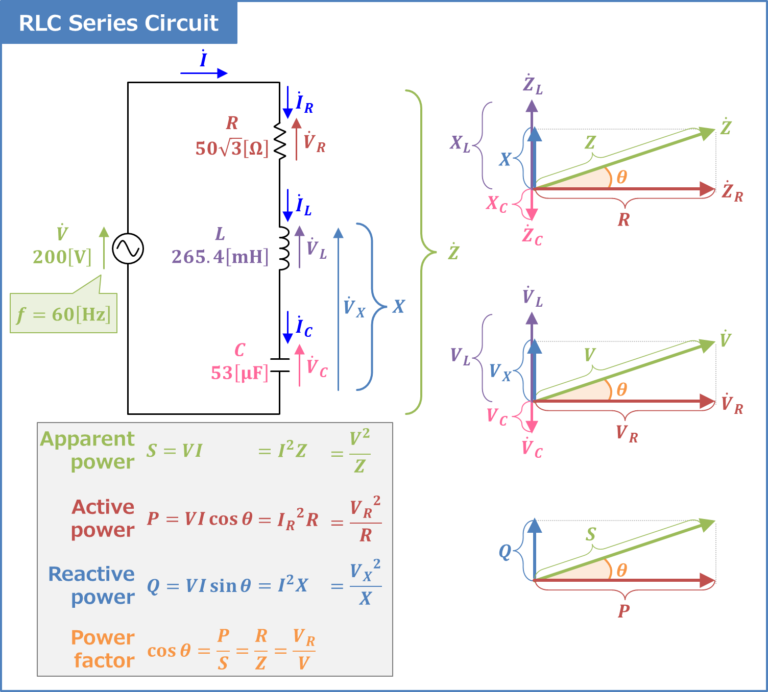
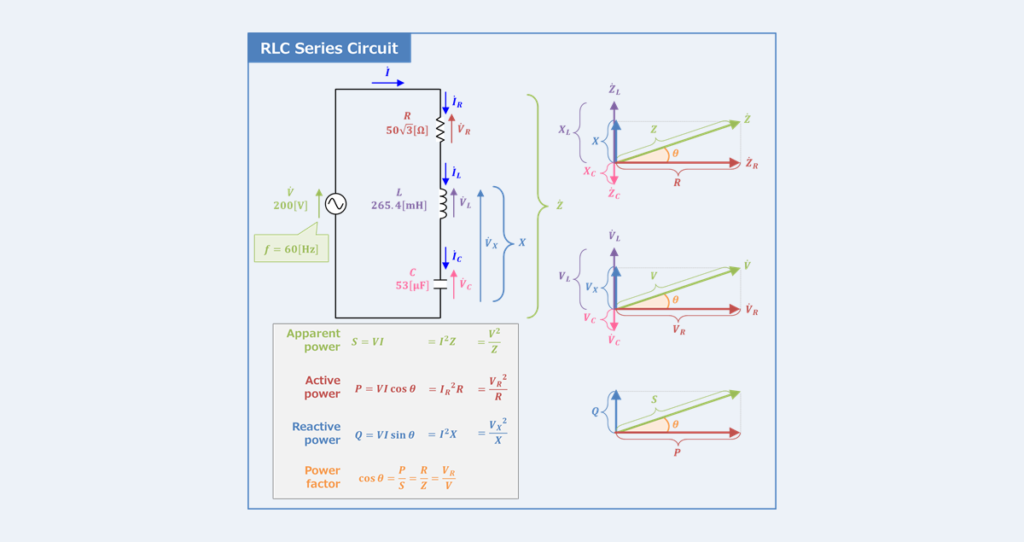
The power factor in RLC circuits is defined as the ratio of real power (measured in watts) to apparent power (measured in volt-amperes). It can be expressed mathematically as:
Power Factor (PF) = Real Power (P) / Apparent Power (S)
In this context, real power refers to the actual power consumed by the circuit to perform work, while apparent power is the product of the current and voltage in the circuit. The power factor can also be expressed in terms of phase angle (φ) between the current and voltage:
Power Factor (PF) = cos(φ)
Why is the Power Factor Important in RLC Circuits?
The power factor is critical for several reasons:
- Efficiency: A higher power factor indicates a more efficient circuit that minimizes energy losses.
- Cost Savings: Many utility companies impose penalties for low power factors, leading to increased operational costs.
- Equipment Longevity: Operating at a higher power factor reduces stress on electrical components, prolonging their lifespan.
- Load Management: Understanding the power factor helps in better load distribution and management in electrical systems.
How Does the RLC Circuit Affect Power Factor?
The relationship between resistance, inductance, and capacitance in an RLC circuit has a direct impact on the power factor. Here’s how each component influences the power factor:
Read also:Unleash The Thrill Sun Ski Sports For Ultimate Adventure
- Resistor (R): It consumes real power and contributes positively to the power factor.
- Inductor (L): It creates a lagging current, which decreases the power factor.
- Capacitor (C): It creates a leading current, which can improve the power factor if appropriately sized.
What are the Common Issues Related to Low Power Factor?
A low power factor can cause several issues, including:
- Increased Energy Costs: Utilities may charge extra fees for low power factors.
- Reduced System Capacity: Low power factor can reduce the overall capacity of the electrical system.
- Overheating: Equipment may overheat due to the increased current required to deliver the same amount of power.
- Voltage Drops: Low power factor can lead to significant voltage drops, affecting the performance of electrical devices.
How Can the Power Factor of RLC Circuit be Improved?
Improving the power factor of RLC circuits can be achieved through various methods:
- Power Factor Correction Capacitors: Adding capacitors to counteract inductive loads.
- Adjusting Load Types: Replacing inductive loads with more resistive loads when possible.
- Using Synchronous Condensers: These machines can adjust reactive power dynamically.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensuring all components are functioning correctly to avoid unnecessary losses.
What are the Calculation Methods for Power Factor in RLC Circuits?
Calculating the power factor in RLC circuits involves several steps. Here’s a basic outline:
- Measure the voltage (V) and current (I) in the circuit.
- Calculate the real power (P) using the formula: P = V x I x PF.
- Calculate the apparent power (S) using the formula: S = V x I.
- Determine the power factor using the formula: PF = P / S.
Conclusion: The Significance of Managing Power Factor in RLC Circuits
Understanding and managing the power factor of RLC circuit is essential for optimizing energy usage and ensuring the longevity of electrical systems. By implementing corrective measures and regularly assessing the power factor, industries and households can save money, enhance efficiency, and improve overall system performance. As technology advances, the importance of power factor management will continue to grow, making it a vital aspect of electrical engineering and energy management.
Article Recommendations