The Comprehensive Guide To Understanding RCS Messaging
What does RCS message mean? If you've ever wondered about the future of text messaging, then you may have come across the term RCS, or Rich Communication Services. RCS is being hailed as the next big thing in messaging technology, promising to enhance the way we communicate on our mobile devices. But what exactly is RCS, and how does it differ from traditional SMS and MMS messaging? In this article, we will delve into the world of RCS messaging, exploring its features, benefits, and implications for users worldwide.
As smartphone users, we've become accustomed to the limitations of SMS and MMS, such as character restrictions, lack of multimedia support, and inconsistent delivery reports. RCS aims to address these issues by offering a more dynamic and feature-rich messaging experience. With RCS, users can enjoy functionalities like read receipts, typing indicators, and higher-quality image sharing, all within the familiar interface of their default messaging app. But how does RCS work, and what does it mean for the future of communication?
The adoption of RCS has been steadily growing, with major carriers and tech companies like Google championing its implementation. As more devices and networks support RCS, the messaging landscape is poised for a significant shift. While there are still challenges to overcome, such as universal compatibility and security concerns, RCS has the potential to revolutionize the way we connect with one another. In this article, we will explore the technical aspects of RCS, its current status in the market, and its potential impact on consumers and businesses alike.
Read also:Uncovering The Significance Of If My People Who Are Called
Table of Contents
- Introduction to RCS Messaging
- The Evolution of Messaging
- How RCS Messaging Works
- Key Features of RCS
- Comparison with SMS and MMS
- Benefits of RCS for Users
- Challenges and Limitations
- Security and Privacy Concerns
- The Future of RCS Messaging
- Adoption and Support
- Impact on Business Communications
- Global Implementation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction to RCS Messaging
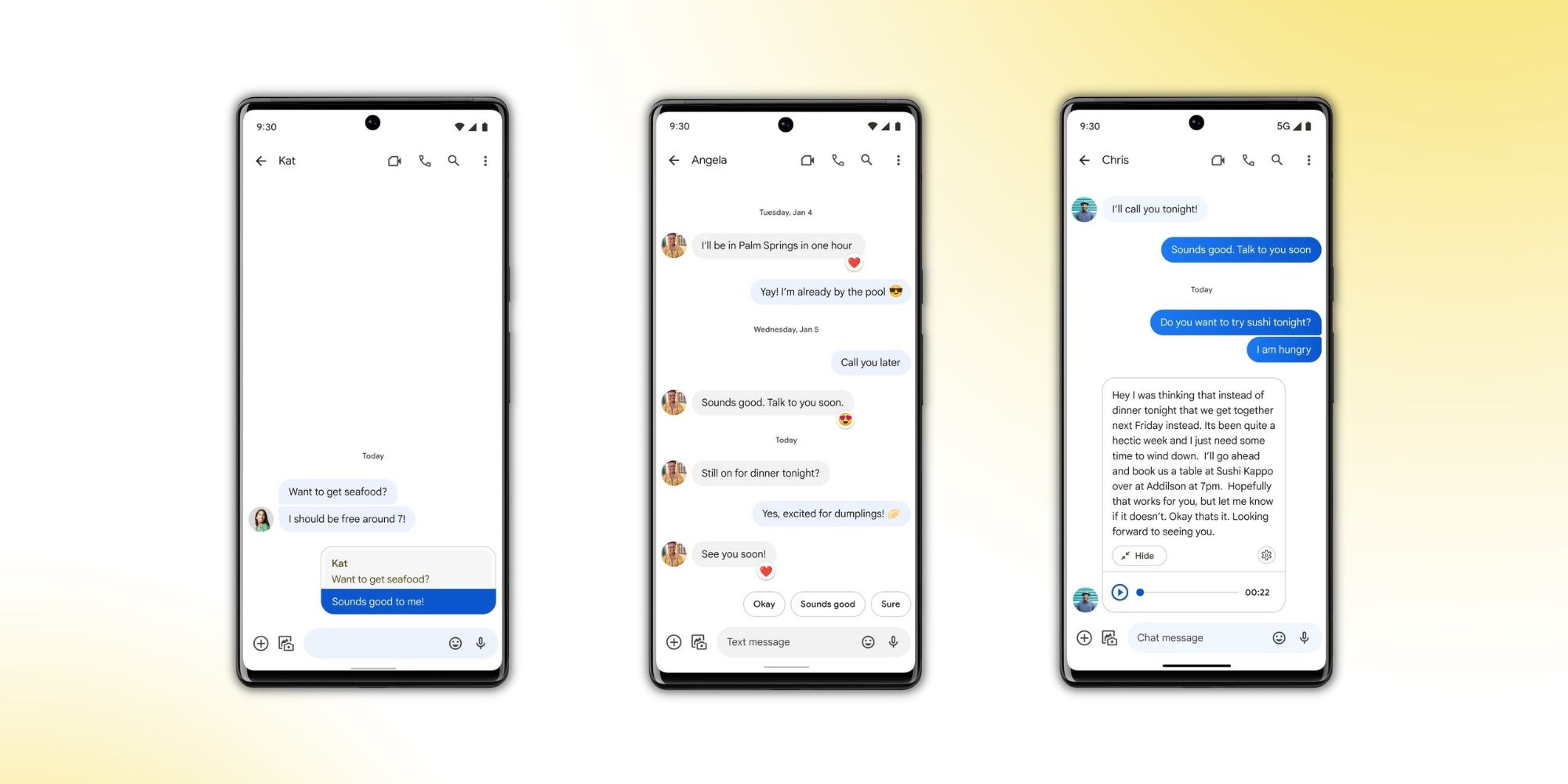
Rich Communication Services (RCS) is an innovative protocol designed to improve the messaging experience on mobile devices. Unlike traditional SMS and MMS, RCS enables users to send messages that are not limited to text but can include a variety of multimedia content, such as high-resolution images, videos, and audio messages. RCS also supports advanced features like group chat, file transfer, location sharing, and contact sharing.
The development of RCS began as a collaborative effort among industry stakeholders to create a universal messaging standard that could rival over-the-top (OTT) messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and iMessage. The goal was to provide users with a seamless and rich communication experience directly through their native messaging apps, without the need to rely on third-party services.
RCS has been standardized by the GSM Association (GSMA), an organization that represents the interests of mobile operators worldwide. The GSMA's Universal Profile, a set of standards for RCS, ensures interoperability across different devices and networks, making it easier for users to communicate regardless of their carrier or device manufacturer.
The Evolution of Messaging
Messaging has come a long way since the early days of mobile communication. The first SMS (Short Message Service) was sent in 1992, revolutionizing the way people communicated by allowing short text messages to be sent between mobile phones. However, the limitations of SMS, such as the 160-character limit and lack of multimedia support, soon became apparent as technology advanced.
In response to these limitations, MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) was introduced in the early 2000s, allowing users to send images, videos, and audio files. However, MMS was often plagued by issues such as high costs, slow delivery times, and compatibility problems between different devices and networks.
The rise of smartphones and mobile internet access paved the way for OTT messaging apps, which offered users a more robust and flexible messaging experience. Apps like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and iMessage capitalized on the shortcomings of SMS and MMS by providing features such as free messaging over Wi-Fi or mobile data, multimedia support, and enhanced privacy options. As a result, traditional messaging services began to lose ground to these OTT platforms.
Read also:Unleash The Magic Dance Captivatingly With Ungliyon Par Usko Nachana
How RCS Messaging Works
RCS messaging operates over the internet rather than through traditional cellular networks, similar to OTT messaging apps. This enables the transmission of rich media content and advanced features that are not possible with SMS and MMS. RCS messages are sent using data, either mobile data or Wi-Fi, and rely on IP-based communication protocols for delivery.
One of the key components of RCS is the Universal Profile, which defines a set of standardized features and capabilities that all RCS-enabled devices and networks must support. This ensures that users can enjoy a consistent messaging experience, regardless of their carrier or device manufacturer. The Universal Profile includes functionalities like read receipts, typing indicators, group chat, and file sharing, among others.
To use RCS, both the sender and recipient must have RCS-enabled devices and be connected to an RCS-supported network. If either party does not meet these criteria, the message will default to SMS or MMS, ensuring that communication is not disrupted. This seamless fallback mechanism is one of the reasons why RCS is considered a viable successor to traditional messaging services.
Key Features of RCS
RCS offers a range of features that enhance the messaging experience, making it a compelling alternative to traditional SMS and MMS. Some of the key features of RCS include:
- Rich Media Messaging: Users can send high-resolution images, videos, audio files, and documents, providing a more engaging communication experience.
- Read Receipts: RCS allows users to see when their messages have been read by the recipient, similar to OTT messaging apps.
- Typing Indicators: Users can see when someone is typing a response, adding a sense of immediacy and engagement to conversations.
- Group Chat: RCS supports group chats with multiple participants, making it easier for users to communicate with friends, family, and colleagues.
- Location Sharing: Users can share their real-time location with others, facilitating meetups and providing peace of mind.
- File Transfer: RCS enables users to send and receive various file types, including PDFs and Word documents.
Comparison with SMS and MMS
While SMS and MMS have been the standard for mobile messaging for many years, they have several limitations that RCS addresses. Here's a comparison of RCS with SMS and MMS:
- Character Limit: SMS is limited to 160 characters per message, while RCS allows for longer, more detailed messages.
- Media Support: MMS supports images, videos, and audio, but often at reduced quality. RCS allows for high-resolution media sharing without degradation.
- Delivery Confirmation: SMS and MMS do not provide delivery or read receipts, whereas RCS offers both, enhancing communication transparency.
- Cost: SMS and MMS can incur charges based on the number of messages or data used, while RCS messages are sent over data, potentially reducing costs for users with data plans.
- Interactivity: RCS offers features like typing indicators and group chat, which are not available with SMS and MMS.
Benefits of RCS for Users
RCS provides several benefits for users, enhancing the overall messaging experience. Some of the key advantages include:
- Enhanced Communication: With features like rich media messaging, read receipts, and typing indicators, RCS offers a more interactive and engaging communication experience.
- Cost-Effective: By utilizing data for message transmission, RCS can be more cost-effective than SMS and MMS, especially for users with unlimited data plans.
- Seamless Integration: RCS is integrated into the default messaging app on supported devices, eliminating the need for third-party messaging apps and providing a seamless user experience.
- Privacy and Security: RCS supports end-to-end encryption, ensuring that messages remain private and secure between the sender and recipient.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: The Universal Profile ensures that RCS is compatible across different devices and networks, allowing users to communicate without compatibility issues.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, RCS faces several challenges and limitations that have hindered its widespread adoption. Some of these challenges include:
- Universal Adoption: For RCS to be effective, both the sender and recipient must have RCS-enabled devices and be connected to an RCS-supported network. This requirement has slowed down its adoption, as not all carriers and manufacturers support RCS.
- Interoperability Issues: While the Universal Profile aims to ensure interoperability, variations in implementation by carriers and manufacturers can lead to inconsistencies in the user experience.
- Security Concerns: Although RCS supports end-to-end encryption, not all implementations offer this level of security, raising concerns about privacy and data protection.
- Competition from OTT Apps: OTT messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger have a large user base and offer similar features to RCS, making it challenging for RCS to compete.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Security and privacy are critical considerations for any messaging service, and RCS is no exception. While RCS offers enhanced security features compared to SMS and MMS, there are still concerns that need to be addressed:
- End-to-End Encryption: While RCS supports end-to-end encryption, not all implementations offer this feature, leaving messages vulnerable to interception.
- Data Privacy: As RCS messages are transmitted over the internet, there is a risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to user information.
- Carrier and Manufacturer Variability: Differences in how carriers and manufacturers implement RCS can lead to inconsistencies in security features.
The Future of RCS Messaging
The future of RCS messaging looks promising, with ongoing efforts to expand its adoption and address existing challenges. Some of the key developments and trends to watch include:
- Increased Carrier Support: More carriers are expected to adopt RCS, expanding its availability and improving interoperability.
- Enhanced Security Features: Efforts to standardize end-to-end encryption and improve data privacy will strengthen RCS's appeal as a secure messaging option.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: RCS may integrate with emerging technologies like 5G and IoT, offering new opportunities for innovation and enhanced user experiences.
- Business Applications: RCS's rich media capabilities and advanced features make it an attractive option for business communications, enabling new opportunities for customer engagement and support.
Adoption and Support
The adoption and support of RCS messaging have been steadily increasing, with more carriers and device manufacturers embracing the technology. Some of the factors driving adoption include:
- Carrier Collaboration: Collaborative efforts among carriers to implement the Universal Profile have improved interoperability and expanded RCS's reach.
- Device Manufacturer Support: Major smartphone manufacturers, such as Samsung and Google, have integrated RCS into their devices, making it more accessible to users.
- Consumer Demand: As consumers seek more advanced messaging features, RCS offers a compelling alternative to traditional messaging services.
Impact on Business Communications
RCS messaging has the potential to transform business communications by offering new ways to engage with customers and enhance customer service. Some of the benefits for businesses include:
- Rich Media Interactions: Businesses can use RCS to send rich media content, such as product images, videos, and promotions, directly to customers.
- Improved Customer Engagement: Features like read receipts and typing indicators enable businesses to engage with customers in real-time, improving communication and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Customer Support: RCS's multimedia capabilities allow businesses to offer more effective customer support, such as sharing troubleshooting guides or video tutorials.
Global Implementation
The global implementation of RCS messaging is an ongoing process, with varying levels of adoption across different regions. Some of the key considerations for global implementation include:
- Regional Variability: Differences in carrier support, regulatory environments, and consumer preferences can impact RCS adoption in different regions.
- International Collaboration: Efforts to promote international collaboration and standardization are essential for ensuring consistent RCS experiences worldwide.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in infrastructure development, such as expanding 4G and 5G networks, will support the global rollout of RCS.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is RCS messaging? RCS (Rich Communication Services) is a protocol designed to enhance the messaging experience by offering features like rich media messaging, read receipts, and group chat.
- How does RCS differ from SMS and MMS? Unlike SMS and MMS, RCS supports advanced features like high-resolution media sharing, read receipts, typing indicators, and more, offering a richer and more interactive communication experience.
- Is RCS messaging secure? RCS offers enhanced security compared to SMS and MMS, but not all implementations support end-to-end encryption. Users should check with their carrier for specific security features.
- Do I need a special app for RCS messaging? RCS is integrated into the default messaging app on supported devices, so no special app is required.
- Can I use RCS messaging internationally? RCS messaging can be used internationally, but both the sender and recipient must have RCS-enabled devices and be connected to RCS-supported networks.
- Will RCS replace OTT messaging apps? While RCS offers similar features to OTT apps, it faces competition from established platforms like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger. RCS's success will depend on its adoption and support from carriers and manufacturers.
Conclusion
RCS messaging represents a significant advancement in mobile communication, offering users a more dynamic and feature-rich messaging experience. With functionalities like rich media messaging, read receipts, and typing indicators, RCS has the potential to revolutionize the way we connect with one another. However, challenges such as universal adoption, security concerns, and competition from OTT apps remain. As more carriers and manufacturers adopt RCS, and as security features continue to improve, RCS is poised to become a compelling alternative to traditional messaging services. Whether you're a casual user or a business looking to enhance customer engagement, RCS offers exciting opportunities for innovation and growth in the messaging landscape.
Article Recommendations